Home > Press > Synchronized dynamic duos: The ability to control how magnetic vortices gyrate together has potential application in magnetic devices
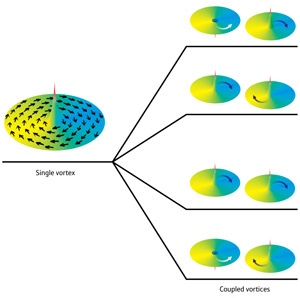 |
| Figure 1: The magnetic domains in a single ferromagnetic disk arrange into a vortex (left). When two disks are brought close together (right), the magnetic vortices begin to move together. Their motion can be in-phase (bottom two levels), or out of phase (top two). The vortex cores can also point in the same direction, or in opposite directions, leading to four possible types of coupled motion. |
Abstract:
Crystals can guide and control light and electricity by creating spatially periodic energy barriers. An electron (or photon) can pass through these barriers only when it has a particular energy, allowing engineers to create switches and other electronic devices. Now, a team of researchers from Japan and India has taken a key step towards using crystals to control waves of magnetic orientation (magnons)1, with the potential to create magnetic analogues to electronic and optical devices, including memory devices and transistors.
Synchronized dynamic duos: The ability to control how magnetic vortices gyrate together has potential application in magnetic devices
Japan | Posted on August 26th, 2011Led by YoshiChika Otani at the RIKEN Advanced Science Institute, Wako, the researchers began by manufacturing tiny disks of ferromagnetic material. The magnetic domains of such disks arrange into vortices (Fig. 1, left), which consist of in-plane circular patterns surrounding a core with out-of-plane magnetization. By applying an alternating current with a particular frequency to such disks, physicists can excite the vortices into a gyrating motion, which they can detect by measuring the voltage across a disk.
Otani and his colleagues found that a current oscillating at 352 megahertz could set the vortex of a single disk into motion. When they brought a second disk near the first one, however, this single resonant frequency split into two: one was lower than the original frequency, and the other was higher. This kind of resonance splitting is characteristic of any pair of interacting oscillators with similar energies, whether it be two molecules that are covalently bonded to each other, or two swinging pendula.
The frequency splitting observed in the researchers' pair of disks indicated that the magnetic vortices in each were coupled together, even though the current was driving one disk only. The researchers showed through numerical simulation that the lower-frequency resonance corresponded to the two vortices rotating in phase with each other; the higher-frequency resonance corresponded to an out-of-phase rotation. Depending on whether the core polarizations of the two disks were pointing in the same or opposite directions, Otani and colleagues also observed different frequency pairs. This led to four distinct resonant frequencies in all (Fig. 1, right).
The researchers could control the differences among the four resonant frequencies by changing the distance between disks, as well as the disk sizes. By demonstrating controllable pairing between adjacent magnetic vortices, the results point the way to more complex chains, lattices and crystals in which magnons can be finely controlled, says Otani. "Our next target is to engineer a structure in which macroscopic spin waves propagate only along particular crystallographic directions."
The corresponding author for this highlight is based at the Quantum Nano-Scale Magnetics Team, RIKEN Advanced Science Institute
####
About Riken Research
RIKEN is one of Japan’s largest research organizations, with more than 3,000 scientists involved in leading research in centers and institutes across Japan and around the world.
For more information, please click here
Copyright © Riken Research
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Laboratories
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Memory Technology
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








