Home > Press > Simpler way of making proteins could lead to new nanomedicine agents
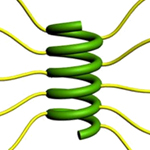 |
| Researchers found that elongating side chains with charged ends enabled short proteins to coil into a stable helix. | Image courtesy Jianjun |
Abstract:
Researchers have developed a simple method of making short protein chains with spiral structures that can also dissolve in water, two desirable traits not often found together. Such structures could have applications as building blocks for self-assembling nanostructures and as agents for drug and gene delivery.
Simpler way of making proteins could lead to new nanomedicine agents
Champaign, IL | Posted on February 22nd, 2011Led by Jianjun Cheng, a professor of materials science and engineering at the University of Illinois, the research team will publish its findings in the Jan. 22 edition of the journal Nature Communications.
Materials scientists have been interested in designing large polymer molecules that could be used as building blocks for self-assembling structures. The challenge has been that the molecules generally adopt a globular, spherical shape, limiting their ability to form orderly aggregates. However, polypeptides - chains of amino acids such as proteins - can form helical structures. Short polypeptide chains that adopt a spiral shape act like cylindrical rods.
"If you have two rigid rods, one positive and one negative, right next to each other, they're going to stick to each other. If you have a way to put the charge on the surface then they can pack together in a close, compact way, so they form a three-dimensional structure," Cheng said.
However, it is difficult to make helical polypeptides that are water-soluble so they can be used in solution. Polypeptides gain their solubility from side chains - molecular structures that stem from each amino acid link in the polypeptide chain. Amino acids with positive or negative charges in their side chains are needed to make a polypeptide disperse in water.
The problem arises when chains with charged side chains form helical structures. The charges cause a strong repulsion between the side chains, which destabilizes the helical conformation. This causes water-soluble polypeptides to form random coil structures instead of the desired helices.
In exploring solutions to the riddle of helical, water-soluble polypeptides, researchers have tried several complicated methods. For example, scientists have attempted grafting highly water-soluble chemicals to the side chains to increase the polypeptides' overall solubility, or creating helices with charges only on one side.
"You can achieve the helical structure and the solubility but you have to design the helical structure in a very special way. The peptide design needs a very specific sequence. Then you're very limited in the type of polypeptide you can build, and it's not easy to design or handle these polypeptides," Cheng said.
In contrast, Cheng's group developed a very straightforward solution. Since the close proximity of the charges causes the repulsion that disrupts the helix, the researchers simply elongated the side chains, moving the charges farther from the backbone and giving them more freedom to keep their distance from one another.
The researchers observed that as they increased the length of the side chains with charges on the end, the polypeptides' propensity for forming helices also increased.
"It's such a simple idea - move the charge away from the backbone," Cheng said. "It's not difficult at all to make the longer side chains, and it has amazing properties for winding up helical structures simply by pushing the distance between the charge and the backbone."
The group found that not only do polypeptides with long side chains form helices, they display remarkable stability even when compared to non-charged helices. The helices seem immune to temperature, pH, and other denaturing agents that would unwind most polypeptides.
This may explain why amino acids with large hydrophobic side chains are not found in nature. Such immutability would preclude dynamic winding and unwinding of protein structures, which is essential to many biological processes. However, rigid stability is a desirable trait for the types of applications Cheng's group explores: nanostructures for drug and gene delivery, particularly targeting cancerous tumors and stem cells.
"We want to test the correlation of the lengths of the helices and the circulation in the body to see what's the impact of the shape and the charge and the side chains for clearance in the body," Cheng said. "Recent studies show that the aspect ratio of the nanostructures - spherical structures versus tubes - has a huge impact on their penetration of tumor tissues and circulation half-lives in the body."
Cheng plans to create a library of short helical polypeptides of varying backbone lengths, side chain lengths and types of charge. He hopes to simplify the chemistry even further and make the materials widely accessible. His lab already has demonstrated that helical structures can be effective gene delivery and membrane transduction agents, and building the library of soluble helical molecules will allow further investigation of tailoring such nanostructures for specific biomedical applications.
The National Science Foundation and the National Institutes of Health supported this work. Illinois co-authors were graduate students Hua Lu and Yugang Bai and undergraduate student Jason Lang. "Hua Lu, a fifth year graduate student in my group, is the first author of the publication and made the most significant contribution to this work," Cheng said. Yao Lin and Jin Wang, of the University of Connecticut, and professor Shiyong Liu, of the University of Science and Technology of China, also collaborated with Cheng's group on the paper.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Jianjun Cheng
217-244-3924
Copyright © University of Illinois
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Academic/Education
![]() Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
![]() Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Self Assembly
![]() Diamond glitter: A play of colors with artificial DNA crystals May 17th, 2024
Diamond glitter: A play of colors with artificial DNA crystals May 17th, 2024
![]() Liquid crystal templated chiral nanomaterials October 14th, 2022
Liquid crystal templated chiral nanomaterials October 14th, 2022
![]() Nanoclusters self-organize into centimeter-scale hierarchical assemblies April 22nd, 2022
Nanoclusters self-organize into centimeter-scale hierarchical assemblies April 22nd, 2022
![]() Atom by atom: building precise smaller nanoparticles with templates March 4th, 2022
Atom by atom: building precise smaller nanoparticles with templates March 4th, 2022
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








