Home > Press > New lab-on-chip advance uses low-cost, disposable paper strips
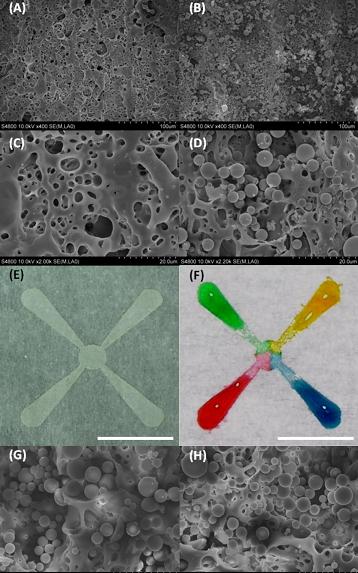 |
| Colored water is used to show how liquid wicks along tiny channels formed in paper using a laser, in research to develop a new technology for medical diagnostics and chemical analysis. Silica microparticles were deposited on patterned areas, allowing liquid to diffuse from one end of a channel to the other. (Birck Nanotechnology Center, Purdue University) |
Abstract:
Researchers have invented a technique that uses inexpensive paper to make "microfluidic" devices for rapid medical diagnostics and chemical analysis.
New lab-on-chip advance uses low-cost, disposable paper strips
West Lafayette, IN | Posted on January 26th, 2011The innovation represents a way to enhance commercially available diagnostic devices that use paper-strip assays like those that test for diabetes and pregnancy.
"With current systems that use paper test strips you can measure things like pH or blood sugar, but you can't perform more complex chemical assays," said Babak Ziaie, a Purdue University professor of electrical and computer engineering and biomedical engineering. "This new approach offers the potential to extend the inexpensive paper-based systems so that they are able to do more complicated multiple analyses on the same piece of paper. It's a generic platform that can be used for a variety of applications."
Findings are detailed in a research paper published online this week in the journal Lab on a Chip.
Current lab-on-a-chip technology is relatively expensive because chips must be specifically designed to perform certain types of chemical analyses, with channels created in glass or plastic and tiny pumps and valves directing the flow of fluids for testing.
The chips are being used for various applications in medicine and research, measuring specific types of cells and molecules in a patient's blood, monitoring microorganisms in the environment and in foods, and separating biological molecules for laboratory analyses. But the chips, which are roughly palm-size or smaller, are difficult to design and manufacture.
The new technique is simpler because the testing platform will be contained on a disposable paper strip containing patterns created by a laser. The researchers start with paper having a hydrophobic - or water-repellant - coating, such as parchment paper or wax paper used for cooking.
"We can buy this paper at any large discount retail store," Ziaie said. "These patterns can be churned out in the millions at very low cost."
A laser is used to burn off the hydrophobic coatings in lines, dots and patterns, exposing the underlying water-absorbing paper only where the patterns are formed.
"Since the hydrophobic agent is already present throughout the thickness of the paper, our method creates islands of hydrophilic patterns," Ziaie said. "This modified surface has a highly porous structure, which helps to trap and localize chemical and biological aqueous reagents for analysis. Furthermore, we've selectively deposited silica microparticles on patterned areas to allow diffusion from one end of a channel to the other."
Those microparticles help to wick liquid to a location where it would combine with another chemical, called a reactant, causing it to change colors and indicating a positive or negative test result.
Having a patterned hydrophilic surface is needed for many detection methods in biochemistry, such as enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, or ELISA, used in immunology to detect the presence of an antibody or an antigen in a sample, Ziaie said.
To demonstrate the new concept, the researchers created paper strips containing arrays of dots dipped in luminol, a chemical that turns fluorescent blue when exposed to blood.
"Then we sprayed blood on the strips, showing the presence of hemoglobin," said Ziaie, whose research is based at the Birck Nanotechnology Center in the university's Discovery Park. "This is just a proof of concept."
Laser modification is known to alter the "wettability" of materials by causing structural and chemical changes to surfaces. However, this treatment has never before been done on paper, he said.
The researchers performed high-resolution imaging and spectroscopic analysis to study the mechanism behind the hydrophobic-hydrophilic conversion of laser-treated parchment paper.
The new approach is within a research area called paper microfluidics.
"Other techniques in paper microfluidics are more complicated," Ziaie said.
For example, other researchers have developed a method that lays down lines of wax or other hydrophobic material on top of untreated, hydrophilic paper.
"Our process is much easier because we just use a laser to create patterns on paper you can purchase commercially and it is already impregnated with hydrophobic material," Ziaie said. "It's a one-step process that could be used to manufacture an inexpensive diagnostic tool for the developing world where people can't afford more expensive analytical technologies."
The strips might be treated with chemicals that cause color changes when exposed to a liquid sample, with different portions of the pattern revealing specific details about the content of the sample. One strip could be used to conduct dozens of tests, he said.
The strips might be inserted into an electronic reader, similar to technology used in conventional glucose testers. Color changes would indicate the presence or absence of specific chemical compounds.
The research paper was written by graduate students Girish Chitnis, Zhenwen Ding and Chun-Li Chang; Cagri A. Savran, an associate professor of mechanical engineering, biomedical engineering and electrical and computer engineering; and Ziaie.
The National Science Foundation funded the work.
The researchers have patented the technique and it is available for licensing through Joseph Trebley, senior project manager for the Purdue Research Foundation Office of Technology Commercialization, at 765-588-3832, (www.prf.org/otc).
ABSTRACT
Laser-treated Hydrophobic Paper: An Inexpensive Microfluidic Platform
Girish Chitnis1,5, Zhenwen Ding2,5, Chun-Li Chang1,5, Cagri A. Savran1,3,4,5 and Babak Ziaie3,4,5,a)
1School of Mechanical Engineering, Purdue University
2Department of Physics, Purdue University, West Lafayette
3School of Electrical and Computer Engineering
4Weldon School of Biomedical Engineering, Purdue University
5Birck Nanotechnology Center, Purdue University
We report a method for fabricating inexpensive microfluidic platforms on paper using laser treatment. Any paper with a hydrophobic surface coating (e.g., parchment paper, wax paper, palette paper) can be used for this purpose. We were able to selectively modify the surface structure and property (hydrophobic to hydrophilic) of several such papers using a CO2 laser. We created patterns down to a minimum feature size of 62±1µm. The modified surface exhibited a highly porous structure which helped to trap/localize chemical and biological aqueous reagents for analysis. The treated surfaces were stable over time and were used to self-assemble arrays of aqueous droplets. Furthermore, we selectively deposited silica microparticles on patterned areas to allow lateral diffusion from one end of a channel to the other. Finally, we demonstrated the applicability of this platform to perform chemical reactions using luminol-based hemoglobin detection.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Writer:
Emil Venere
765-494-4709
Source:
Babak Ziaie
765-494-0725
Copyright © Purdue University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
Microfluidics/Nanofluidics
![]() Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Academic/Education
![]() Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
![]() Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








