Home > Press > UCSB Scientists Demonstrate Biomagnification of Nanomaterials in Simple Food Chain
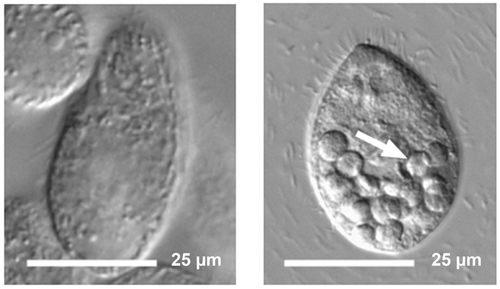 |
| The quantum dot-tainted bacteria stop digestion in the protozoan, and food vacuoles with undigested material accumulate, seen in the right image. This is in contrast to the normal condition of protozoa eating untreated bacteria, seen in the left image. |
Abstract:
An interdisciplinary team of researchers at UC Santa Barbara has produced a groundbreaking study of how nanoparticles are able to biomagnify in a simple microbial food chain.
UCSB Scientists Demonstrate Biomagnification of Nanomaterials in Simple Food Chain
Santa Barbara, CA | Posted on December 20th, 2010"This was a simple scientific curiosity," said Patricia Holden, professor in UCSB's Bren School of Environmental Science & Management and the corresponding author of the study, published in an early online edition of the journal Nature Nanotechnology. "But it is also of great importance to this new field of looking at the interface of nanotechnology and the environment."
Holden's co-authors from UCSB include Eduardo Orias, research professor of genomics with the Department of Molecular, Cellular and Developmental Biology; Galen Stucky, professor of chemistry and biochemistry, and materials; and graduate students, postdoctoral scholars, and staff researchers Rebecca Werlin, Randy Mielke, John Priester, and Peter Stoimenov. Other co-authors are Stephan Krämer, from the California Nanosystems Institute, and Gary Cherr and Susan Jackson, from the UC Davis Bodega Marine Laboratory.
The research was partially funded by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) STAR Program, and by the UC Center for the Environmental Implications of Nanotechnology (UC CEIN), a $24 million collaboration based at UCLA, with researchers from UCSB, UC Davis, UC Riverside, Columbia
University, and other national and international partners. UC CEIN is funded by the National Science Foundation and the EPA.
According to Holden, a prior collaboration with Stucky, Stoimenov, Priester, and Mielke provided the foundation for this research. In that earlier study, the researchers observed that nanoparticles formed from cadmium selenide were entering certain bacteria (called Pseudomonas) and accumulating in them. "We already knew that the bacteria were internalizing these nanoparticles from our previous study," Holden said. "And we also knew that Ed (Orias) and Rebecca (Werlin) were working with a protozoan called Tetrahymena and nanoparticles. So we approached them and asked if they would be interested in a collaboration to evaluate how the protozoan predator is affected by the accumulated nanoparticles inside a bacterial prey." Orias and Werlin credit their interest in nanoparticle toxicity to earlier funding from and participation in the University of California
Toxic Substance Research & Training Program.
The scientists repeated the growth of the bacteria with quantum dots in the new study and and coupled it to a trophic transfer study - the study of the transfer of a compound from a lower to a higher level in a food chain by predation. "We looked at the difference to the predator as it was growing at the expense of different prey types - 'control' prey without any metals, prey that had been grown with a dissolved cadmium salt, and prey that had been grown with cadmium selenide quantum dots," Holden said.
What they found was that the concentration of cadmium increased in the transfer from bacteria to protozoa and, in the process of increasing concentration, the nanoparticles were substantially intact, with very little degradation. "We were able to measure the ratio of the cadmium to the selenium in particles that were inside the protozoa and see that it was substantially the same as in the original nanoparticles that had been used to feed the bacteria," Orias said.
The fact that the ratio of cadmium and selenide was preserved throughout the course of the study indicates that the nanoparticles were themselves biomagnified. "Biomagnification - the increase in concentration of cadmium as the tracer for nanoparticles from prey into predator - this is the first time this has been reported for nanomaterials in an aquatic environment, and furthermore involving microscopic life forms, which comprise the base of all food webs," Holden said.
An implication is that nanoparticles inside the protozoa could then be available to the next level of predators in the food chain, which could lead to broader ecological effects. "These protozoa are greatly enriched in nanoparticles because of feeding on quantum dot-laced bacteria," Hold said. "Because there were toxic effects on the protozoa in this study, there is a concern that there could also be toxic effects higher in the food chain, especially in aquatic environments."
One of the missions of UC CEIN is to try to understand the effects of nanomaterials in the environment, and how scientists can prevent any possible negative effects that might pose a threat to any form of life. "In this context, one might argue that if you could 'design out' whatever property of the quantum dots causes them to enter bacteria, then we could avoid this potential consequence," Holden said. "That would be a positive way of viewing a study like this. Now scientists can look back and say, 'How do we prevent this from happening?'"
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
George Foulsham
(805) 893-3071
Patricia Holden
(805) 893-3195
Eduardo Orias
(805) 893-3024
Copyright © UCSB
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Marine/Watercraft
![]() Strain-sensing smart skin ready to deploy: Nanotube-embedded coating detects threats from wear and tear in large structures July 15th, 2022
Strain-sensing smart skin ready to deploy: Nanotube-embedded coating detects threats from wear and tear in large structures July 15th, 2022
![]() A sunlight-driven “self-healing” anti-corrosion coating May 27th, 2022
A sunlight-driven “self-healing” anti-corrosion coating May 27th, 2022
![]() Quantum tech in space? Scientists design remote monitoring system for inaccessible quantum devices February 11th, 2022
Quantum tech in space? Scientists design remote monitoring system for inaccessible quantum devices February 11th, 2022
Preparing for Nano
![]() Disruptive by Design: Nano Now February 1st, 2019
Disruptive by Design: Nano Now February 1st, 2019
![]() How nanoscience will improve our health and lives in the coming years: Targeted medicine deliveries and increased energy efficiency are just two of many ways October 26th, 2016
How nanoscience will improve our health and lives in the coming years: Targeted medicine deliveries and increased energy efficiency are just two of many ways October 26th, 2016
![]() Searching for a nanotech self-organizing principle May 1st, 2016
Searching for a nanotech self-organizing principle May 1st, 2016
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Academic/Education
![]() Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
![]() Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Environment
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Safety-Nanoparticles/Risk management
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
![]() Closing the gaps — MXene-coating filters can enhance performance and reusability February 28th, 2025
Closing the gaps — MXene-coating filters can enhance performance and reusability February 28th, 2025
Quantum Dots/Rods
![]() A new kind of magnetism November 17th, 2023
A new kind of magnetism November 17th, 2023
![]() IOP Publishing celebrates World Quantum Day with the announcement of a special quantum collection and the winners of two prestigious quantum awards April 14th, 2023
IOP Publishing celebrates World Quantum Day with the announcement of a special quantum collection and the winners of two prestigious quantum awards April 14th, 2023
![]() Qubits on strong stimulants: Researchers find ways to improve the storage time of quantum information in a spin rich material January 27th, 2023
Qubits on strong stimulants: Researchers find ways to improve the storage time of quantum information in a spin rich material January 27th, 2023
![]() NIST’s grid of quantum islands could reveal secrets for powerful technologies November 18th, 2022
NIST’s grid of quantum islands could reveal secrets for powerful technologies November 18th, 2022
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








