 |
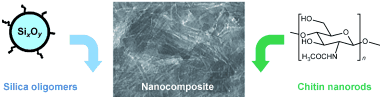
| A new family of chitin–silica nanocomposites has been synthesized by using a versatile colloid-based combination of self-assembly and sol–gel chemistry. Various textures and morphologies can be obtained by adjusting the evaporation-based processes or by applying external fields. After calcination, textures and birefringence are preserved in the resulting mesoporous silicas. |
Abstract:
Chitin-silicon dioxide nanocomposite made by self-organization and sol-gel chemistry
Embedded Rods
Weinheim, Germany | Posted on October 11th, 2010Self-organization processes involving chemical building blocks are the basis for many biological processes and are increasingly of interest in the field of materials synthesis, for example in the production of highly ordered nanocomposites or high-porosity materials with special properties. In the journal Angewandte Chemie, Bruno Alonso and Emmanuel Belamie from the Charles Gerhardt Institute in Montpellier (France) have introduced a novel, highly versatile approach to the large-scale synthesis of a new family of bioorganic-inorganic nanocomposites—with a previously unattainable degree of control over the composition and structure of the materials produced.
Nanocomposites are solid materials made of different substances, one of which is in the form of nanoparticles. The properties of the composites differ significantly from those of the pure individual components. Nanocomposites can also serve as "molds" for the production of porous substances. These have potential application in the areas of gas storage, catalysis, or materials separation.
For their synthesis, the researchers chose to use a sol-gel process, a popular technique for the production of inorganic network structures. In the first step they needed to generate a sol: a suspension of finely divided nanoscopic particles in a solvent. Their challenge was to obtain co-suspension of the two different components, silicon dioxide precursors (siloxane oligomers) and chitin nanorods from shrimp shells (a renewable resource). However, these two components require different conditions to remain in stable suspensions without uncontrolled precipitation. The researchers produced an alcohol suspension by slowly replacing water with ethanol. Through slow removal of the solvent, a gel formed. Gels are gelatinous substances; they contain solid but loose, cross-linked, three-dimensional polymer structures.
The sol can be "poured" into a desired mold and dried or it can be spray-dried into spherical particles. This process results in a nanocomposite made of chitin rods that are fully embedded in a silicon dioxide matrix. The mechanism by which this occurs is based on a self-organized aggregation of the chitin molecules and weak attractive forces between chitin and siloxane oligomers.
The stability of the alcohol suspensions opens up a wide range of possibilities for the production of materials with controllable volume ratios, spatial arrangements, and morphologies. If a magnetic field is applied during preparation of the material, the chitin rods line up in parallel. If the nanocomposite is heated, the chitin rods can be burned off to leave behind cavities. This forms a highly porous material with interesting properties.
Author: Emmanuel Belamie, Institut Charles Gerhardt, Montpellier (France),
Title: Chitin-Silica Nanocomposites by Self-Assembly
Angewandte Chemie International Edition,
Permalink to the article: dx.doi.org/10.1002/anie.201002104
####
For more information, please click here
Copyright © Angewandte Chemie International Edition
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
Chemistry
![]() Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Academic/Education
![]() Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
![]() Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








