Home > Press > “Nanosprings” offer improved performance in biomedicine, electronics
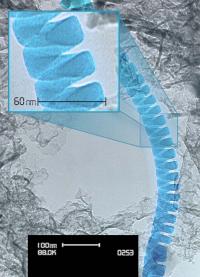 |
| Researchers at Oregon State University have successfully loaded biological molecules onto "nanosprings," an advance that could have many industrial and biomedical applications. (Image by David McIlroy, courtesy of the University of Idaho) |
Abstract:
Researchers at Oregon State University have reported the successful loading of biological molecules onto "nanosprings" - a type of nanostructure that has gained significant interest in recent years for its ability to maximize surface area in microreactors.
By David Stauth
“Nanosprings” offer improved performance in biomedicine, electronics
Corvallis, OR | Posted on September 16th, 2010The findings, announced in the journal Biotechnology Progress, may open the door to important new nanotech applications in production of pharmaceuticals, biological sensors, biomedicine or other areas.
"Nanosprings are a fairly new concept in nanotechnology because they create a lot of surface area at the same time they allow easy movement of fluids," said Christine Kelly, an associate professor in the School of Chemical, Biological and Environmental Engineering at OSU.
"They're a little like a miniature version of an old-fashioned, curled-up phone cord," Kelly said. "They make a great support on which to place reactive catalysts, and there are a variety of potential applications."
The OSU researchers found a way to attach enzymes to silicon dioxide nanosprings in a way that they will function as a biological catalyst to facilitate other chemical reactions. They might be used, for instance, to create a biochemical sensor that can react to a toxin far more quickly than other approaches.
"The ability to attach biomolecules on these nanosprings, in an efficient and environmentally friendly way, could be important for a variety of sensors, microreactors and other manufacturing applications," said Karl Schilke, an OSU graduate student in chemical engineering and principal investigator on the study.
The work was done in collaboration with the University of Idaho Department of Physics and GoNano Technologies of Moscow, Idaho, a commercial producer of nanosprings. Nanosprings are being explored for such uses as hydrogen storage, carbon cycling and lab-on-chip electronic devices. The research was also facilitated by the Microproducts Breakthrough Institute, a collaboration of OSU and the Pacific Northwest National Laboratory.
"An increasingly important aspect of microreactor and biosensor technology is the development of supports that can be easily coated with enzymes, antibodies, or other biomolecules," the researchers wrote in their report.
"These requirements are neatly met by nanosprings, structures that can be grown by a chemical vapor deposition process on a wide variety of surfaces," they said. "This study represents the first published application of nanosprings as a novel and highly efficient carrier for immobilized enzymes in microreactors."
####
About OSU College of Engineering
The OSU College of Engineering is among the nation¹s largest and most productive engineering programs. In the past six years, the College has more than doubled its research expenditures to $27.5 million by emphasizing highly collaborative research that solves global problems, spins out new companies, and produces opportunity for students through hands-on learning.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Christine Kelly
541-737-6755
Copyright © OSU College of Engineering
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Academic/Education
![]() Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
![]() Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








