Home > Press > First graphene touchscreen
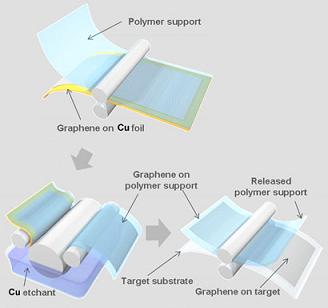 |
| The researchers built up a graphene layer on copper foil and then used rollers to transfer the graphene to a polymer support and then onto a final substrate. © Nature Nanotechnology |
Abstract:
Researchers in Korea and Japan have fabricated films of graphene - planar sheets of carbon one atom thick - measuring tens of centimetres. The researchers engineered these large graphene films into transparent electrodes, which were incorporated into touchscreen panel devices.
By Simon Hadlington
First graphene touchscreen
UK | Posted on June 22nd, 2010The new work represents another milestone in the astonishing technological advance of graphene from its initial isolation only a few years ago. Experts predict that graphene will be found in consumer products within a couple of years.
The team, led by Jong-Hyun Ahn and Byung Hee Hong of Sungkyunkwan University, Korea, grew a graphene layer on copper foil by chemical vapour deposition (CVD) using a previously demonstrated technique.
Using a roller, the graphene face can then be pressed against an adhesive polymer support and the copper etched away, leaving the graphene film attached to the polymer. The graphene can then be pressed against a final substrate - such as polyethylene terephthalate (PET) - again using rollers, and the polymer adhesive released by heating. Subsequent layers of graphene can then be added in a similar way.
The researchers used this technique to create a rectangular graphene film measuring 30 inches (76 cm) in the diagonal. The graphene was doped by treating with nitric acid and in this form the graphene sheet can act as a large, transparent electrode and was demonstrated to work in a touchscreen device.
Typically, transparent electrodes used in such applications are made from indium tin oxides (ITO). The researchers say that the graphene electrode has better transparency and is tougher. 'The price of indium has increased by a few times over the past decades and this will be more serious as markets for display and solar cells expand,' says Ahn.'In addition, oxide materials like ITO are usually fragile and weak.' Because of this, ITO-based touchscreens have a finite life span, whereas, says Ahn, a graphene-based screen should last essentially forever.
'In addition, the graphene production needs just a tiny amount of carbon sources without any rare materials, and the copper substrate is recyclable, so it is much more environmentally friendly than ITO production.'
Andre Geim of the University of Manchester in the UK, who is widely credited as being the founding father of modern graphene science having discovered isolated graphene around five years ago, says the new work demonstrates the astonishing rapidity with which graphene technology has advanced. 'This clearly shows that graphene is no longer wishful thinking as far as industrial applications go. People have gone from lab-scale to industrial-scale production unbelievably quickly. Within two years we will have consumer products.'
####
For more information, please click here
Copyright © Royal Society of Chemistry
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Display technology/LEDs/SS Lighting/OLEDs
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() Efficient and stable hybrid perovskite-organic light-emitting diodes with external quantum efficiency exceeding 40 per cent July 5th, 2024
Efficient and stable hybrid perovskite-organic light-emitting diodes with external quantum efficiency exceeding 40 per cent July 5th, 2024
Videos/Movies
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Academic/Education
![]() Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
![]() Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Nanotubes/Buckyballs/Fullerenes/Nanorods/Nanostrings/Nanosheets
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








