Home > Press > How butterflies’ wings could cut bank fraud
 |
Abstract:
Cambridge scientists have discovered a way of mimicking the stunningly bright and beautiful colours found on the wings of tropical butterflies. The findings could have important applications in the security printing industry, helping to make bank notes and credit cards harder to forge.
How butterflies’ wings could cut bank fraud
Cambridge, UK | Posted on May 31st, 2010The striking iridescent colours displayed on beetles, butterflies and other insects have long fascinated both physicists and biologists, but mimicking nature's most colourful, eye-catching surfaces has proved elusive.
This is partly because rather than relying on pigments, these colours are produced by light bouncing off microscopic structures on the insects' wings.
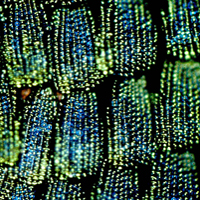
Mathias Kolle, working with Professor Ullrich Steiner and Professor Jeremy Baumberg of the University of Cambridge, studied the Indonesian Peacock or Swallowtail butterfly (Papilio blumei), whose wing scales are composed of intricate, microscopic structures that resemble the inside of an egg carton.
Because of their shape and the fact that they are made up of alternate layers of cuticle and air, these structures produce intense colours.
Using a combination of nanofabrication procedures - including self-assembly and atomic layer deposition - Kolle and his colleagues made structurally identical copies of the butterfly scales, and these copies produced the same vivid colours as the butterflies' wings.
According to Kolle: "We have unlocked one of nature's secrets and combined this knowledge with state-of-the-art nanofabrication to mimic the intricate optical designs found in nature."
"Although nature is better at self-assembly than we are, we have the advantage that we can use a wider variety of artificial, custom-made materials to optimise our optical structures."
As well as helping scientists gain a deeper understanding of the physics behind these butterflies' colours, being able to mimic them has promising applications in security printing.
"These artificial structures could be used to encrypt information in optical signatures on banknotes or other valuable items to protect them against forgery. We still need to refine our system but in future we could see structures based on butterflies wings shining from a £10 note or even our passports," he says.
Intriguingly, the butterfly may also be using its colours to encrypt itself - appearing one colour to potential mates but another colour to predators.
Kolle explains: "The shiny green patches on this tropical butterfly's wing scales are a stunning example of nature's ingenuity in optical design. Seen with the right optical equipment these patches appear bright blue, but with the naked eye they appear green.
"This could explain why the butterfly has evolved this way of producing colour. If its eyes see fellow butterflies as bright blue, while predators only see green patches in a green tropical environment, then it can hide from predators at the same time as remaining visible to members of its own species."
The results are published today in Nature Nanotechnology.
The research was funded by the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council and the Cambridge Newton Trust.
####
For more information, please click here
Copyright © University of Cambridge
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Videos/Movies
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Law enforcement/Anti-Counterfeiting/Security/Loss prevention
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Academic/Education
![]() Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
![]() Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Self Assembly
![]() Diamond glitter: A play of colors with artificial DNA crystals May 17th, 2024
Diamond glitter: A play of colors with artificial DNA crystals May 17th, 2024
![]() Liquid crystal templated chiral nanomaterials October 14th, 2022
Liquid crystal templated chiral nanomaterials October 14th, 2022
![]() Nanoclusters self-organize into centimeter-scale hierarchical assemblies April 22nd, 2022
Nanoclusters self-organize into centimeter-scale hierarchical assemblies April 22nd, 2022
![]() Atom by atom: building precise smaller nanoparticles with templates March 4th, 2022
Atom by atom: building precise smaller nanoparticles with templates March 4th, 2022
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








