Home > Press > Brown Chemists Report Promising Advance in Fuel-Cell Technology
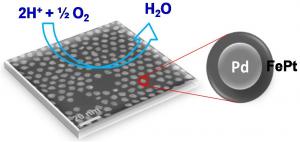 |
| Less platinum, better efficiency The multimetallic nanoparticle created by Brown University chemists for fuel-cell reactions uses a palladium core and an iron-platinum shell. Credit: Sun Lab/Brown University |
Abstract:
Chemists at Brown University have come up with a promising advance in fuel-cell technology. The team has demonstrated that a nanoparticle with a palladium core and an iron-platinum shell outperforms commercially available pure-platinum catalysts and lasts longer. The finding, reported in the Journal of the American Chemical Society, could move fuel cells a step closer to reality.
Brown Chemists Report Promising Advance in Fuel-Cell Technology
Providence, RI | Posted on May 25th, 2010Creating catalysts that can operate efficiently and last a long time is a big barrier to taking fuel-cell technology from the lab bench to the assembly line. The precious metal platinum has been the choice for many researchers, but platinum has two major downsides: It is expensive, and it breaks down over time in fuel-cell reactions.
In a new study, chemists at Brown University report a promising advance. They have created a unique core and shell nanoparticle that uses far less platinum yet performs more efficiently and lasts longer than commercially available pure-platinum catalysts at the cathode end of fuel-cell reactions.
The chemistry known as oxygen reduction reaction takes place at the fuel cell's cathode, creating water as its only waste, rather than the global-warming carbon dioxide produced by internal combustion systems. The cathode is also where up to 40 percent of a fuel cell's efficiency is lost, so "this is a crucial step in making fuel cells a more competitive technology with internal combustion engines and batteries," said Shouheng Sun, professor of chemistry at Brown and co-author of the paper in the Journal of the American Chemical Society.
The research team, which includes Brown graduate student and co-author Vismadeb Mazumder and researchers from Oak Ridge National Laboratory in Tennessee, created a five-nanometer palladium (Pd) core and encircled it with a shell consisting of iron and platinum (FePt). The trick, Mazumder said, was in molding a shell that would retain its shape and require the smallest amount of platinum to pull off an efficient reaction. The team created the iron-platinum shell by decomposing iron pentacarbonyl [Fe(CO)5] and reducing platinum acetylacetonate [Pt(acac)2], a technique Sun first reported in a 2000 Science paper. The result was a shell that uses only 30 percent platinum, although the researchers say they expect they will be able to make thinner shells and use even less platinum.
"If we don't use iron pentacarbonyl, then the platinum doesn't form on the (palladium) core," Mazumder said.
The researchers demonstrated for the first time that they could consistently produce the unique core-shell structures. In laboratory tests, the palladium/iron-platinum nanoparticles generated 12 times more current than commercially available pure-platinum catalysts at the same catalyst weight. The output also remained consistent over 10,000 cycles, at least ten times longer than commercially available platinum models that begin to deteriorate after 1,000 cycles.
The team created iron-platinum shells that varied in width from one to three nanometers. In lab tests, the group found the one-nanometer shells performed best.
"This is a very good demonstration that catalysts with a core and a shell can be made readily in half-gram quantities in the lab, they're active, and they last," Mazumder said. "The next step is to scale them up for commercial use, and we are confident we'll be able to do that."
Mazumder and Sun are studying why the palladium core increases the catalytic abilities of iron platinum, although they think it has something to do with the transfer of electrons between the core and shell metals. To that end, they are trying to use a chemically more active metal than palladium as the core to confirm the transfer of electrons in the core-shell arrangement and its importance to the catalyst's function.
Miaofang Chi and Karren More at the Oak Ridge Laboratory also contributed to the paper. The U.S. Department of Energy's Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy funded the research as part of its Fuel Cell Technologies Program.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Richard Lewis
(401) 863-3766
Copyright © Brown University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
Chemistry
![]() Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Academic/Education
![]() Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
![]() Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Fuel Cells
![]() Deciphering local microstrain-induced optimization of asymmetric Fe single atomic sites for efficient oxygen reduction August 8th, 2025
Deciphering local microstrain-induced optimization of asymmetric Fe single atomic sites for efficient oxygen reduction August 8th, 2025
![]() Current and Future Developments in Nanomaterials and Carbon Nanotubes: Applications of Nanomaterials in Energy Storage and Electronics October 28th, 2022
Current and Future Developments in Nanomaterials and Carbon Nanotubes: Applications of Nanomaterials in Energy Storage and Electronics October 28th, 2022
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








