Home > Press > Physicists capture first images of atomic spin
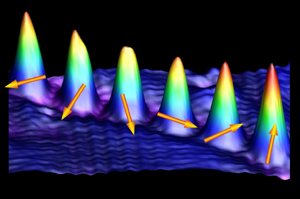 |
| The different shape and appearance of these individual cobalt atoms is caused by the different spin directions. (Image courtesy Saw-Wai Hla, Ohio University) |
Abstract:
Discovery supports development of nanoscale magnetic storage devices
Physicists capture first images of atomic spin
Athens, OH | Posted on April 28th, 2010Though scientists argue that the emerging technology of spintronics may trump conventional electronics for building the next generation of faster, smaller, more efficient computers and high-tech devices, no one has actually seen the spin—a quantum mechanical property of electrons—in individual atoms until now.
In a study published as an Advance Online Publication in the journal Nature Nanotechnology on Sunday, physicists at Ohio University and the University of Hamburg in Germany present the first images of spin in action.
The researchers used a custom-built microscope with an iron-coated tip to manipulate cobalt atoms on a plate of manganese. Through scanning tunneling microscopy, the team repositioned individual cobalt atoms on a surface that changed the direction of the electrons' spin. Images captured by the scientists showed that the atoms appeared as a single protrusion if the spin direction was upward, and as double protrusions with equal heights when the spin direction was downward.
The study suggests that scientists can observe and manipulate spin, a finding that may impact future development of nanoscale magnetic storage, quantum computers and spintronic devices.
"Different directions in spin can mean different states for data storage," said Saw-Wai Hla, an associate professor of physics and astronomy in Ohio University's Nanoscale and Quantum Phenomena Institute and one of the primary investigators on the study. "The memory devices of current computers involve tens of thousands of atoms. In the future, we may be able to use one atom and change the power of the computer by the thousands."
Unlike electronic devices, which give off heat, spintronic-based devices are expected to experience less power dissipation.
The experiments were conducted in an ultra-high vacuum at the low temperature of 10 Kelvin, with the use of liquid helium. Researchers will need to observe the phenomenon at room temperature before it can be used in computer hard drives.
But the new study suggests a path to that application, said study lead author Andre Kubetzka of the University of Hamburg. To image spin direction, the team not only used a new technique but also a manganese surface with a spin that, in turn, allowed the scientists to manipulate the spin of the cobalt atoms under study.
"The combination of atom manipulation and spin sensitivity gives a new perspective of constructing atomic-scale structures and investigating their magnetic properties," Kubetzka said.
The research, which was carried out at the University of Hamburg, was supported by the German Research Foundation and a Partnership for International Collaboration and Education (PIRE) grant from National Science Foundation.
The research is the result of a collaboration among three research teams: a spin-polarized scanning tunneling microscopy group of Professor Roland Wiesendanger led by Kubetzka at the University of Hamburg, Germany; Hla, an expert in atom manipulation at Ohio University; and two theorists, Professor Stefan Heinze and Paolo Ferriani, now at the Christian-Albrechts-Universität Kiel, in Germany.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Saw-Wai Hla
(740) 593-1727
Andrea Gibson
director of research communications (740) 597-2166
Copyright © Ohio University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Academic/Education
![]() Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
![]() Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Spintronics
![]() Quantum materials: Electron spin measured for the first time June 9th, 2023
Quantum materials: Electron spin measured for the first time June 9th, 2023
Memory Technology
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








