Home > Press > NIST-Cornell Team Builds World's First Nanofluidic Device with Complex 3-D Surfaces
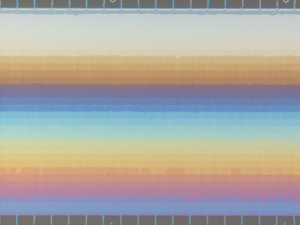 |
| Overhead view of the NIST-Cornell 3-D nanofluidic device showing the different depth levels within the chamber as horizontal bands. The deepest, at the bottom, measures about 620 nanometers (slightly smaller than an average bacterium), while the shallowest, at the top, is about 60 nanometers (1,000 times smaller than the width of a human hair). The colors of the bands result from different mixing of white light components (interference) at each depth. |
Abstract:
Chamber Separates Nanoparticles Like a ‘Coin Sorter'
NIST-Cornell Team Builds World's First Nanofluidic Device with Complex 3-D Surfaces
Gaithersburg, MD | Posted on March 31st, 2009Researchers at the Commerce Department's National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) and Cornell University have capitalized on a process for manufacturing integrated circuits at the nanometer (billionth of a meter) level and used it to develop a method for engineering the first-ever nanoscale fluidic (nanofluidic) device with complex three-dimensional surfaces. As described in a paper published online today in the journal Nanotechnology*, the Lilliputian chamber is a prototype for future tools with custom-designed surfaces to manipulate and measure different types of nanoparticles in solution.
Among the potential applications for this technology: the processing of nanomaterials for manufacturing; the separation and measuring of complex nanoparticle mixtures for drug delivery, gene therapy and nanoparticle toxicology; and the isolation and confinement of individual DNA strands for scientific study as they are forced to unwind and elongate (DNA typically coils into a ball-like shape in solution) within the shallowest passages of the device.
Nanofluidic devices are usually fabricated by etching tiny channels into a glass or silicon wafer with the same lithographic procedures used to manufacture circuit patterns on computer chips. These flat rectangular channels are then topped with a glass cover that is bonded in place. Because of the limitations inherent to conventional nanofabrication processes, almost all nanofluidic devices to date have had simple geometries with only a few depths. This limits their ability to separate mixtures of nanoparticles with different sizes or study the nanoscale behavior of biomolecules (such as DNA) in detail.
To solve the problem, NIST's Samuel Stavis and Michael Gaitan teamed with Cornell's Elizabeth Strychalski to develop a lithographic process to fabricate nanofluidic devices with complex 3-D surfaces. As a demonstration of their method, the researchers constructed a nanofluidic chamber with a "staircase" geometry etched into the floor. The "steps" in this staircase—each level giving the device a progressively increasing depth from 10 nanometers (approximately 6,000 times smaller than the width of a human hair) at the top to 620 nanometers (slightly smaller than an average bacterium) at the bottom—are what give the device its ability to manipulate nanoparticles by size in the same way a coin sorter separates nickels, dimes and quarters.
The NIST-Cornell nanofabrication process utilizes grayscale photolithography to build 3-D nanofluidic devices. Photolithography has been used for decades by the semiconductor industry to harness the power of light to engrave microcircuit patterns onto a chip. Circuit patterns are defined by templates, or photomasks, that permit different amounts of light to activate a photosensitive chemical, or photoresist, sitting atop the chip material, or substrate.
Conventional photolithography uses photomasks as "black-or-white stencils" to remove either all or none of the photoresist according to a set pattern. The "white" parts of the pattern—those that let light through—are then etched to a single depth into the substrate. Grayscale photolithography, on the other hand, uses "shades of gray" to activate and sculpt the photoresist in three dimensions. In other words, light is transmitted through the photomask in varying degrees according to the "shades" defined in the pattern. The amount of light permitted through determines the amount of exposure of the photoresist, and, in turn, the amount of photosensitive chemical removed after development.
The NIST-Cornell nanofabrication process takes advantage of this characteristic, allowing the researchers to transfer a 3-D pattern for nanochannels of numerous depths into a glass substrate with nanometer precision using a single etch.
The result is the "staircase" that gives the 3-D nanofluidic device its versatility.
Size exclusion of nanoparticles and confinement of individual DNA strands in the 3-D nanofluidic device is accomplished using electrophoresis, the method of moving charged particles through a solution by forcing them forward with an applied electric field. In these novel experiments, the NIST-Cornell researchers tested their device with two different solutions: one containing 100-nanometer-diameter polystyrene spheres and the other containing 20-micrometer (millionth of a meter)-length DNA molecules from a virus that infects the common bacterium Escherichia coli. In each experiment, the solution was injected into the deep end of the chamber and then electrophoretically driven across the device from deeper to shallower levels. Both the spheres and DNA strands were tagged with fluorescent dye so that their movements could be tracked with a microscope.
In the trials using rigid nanoparticles, the region of the 3-D nanofluidic device where the channels were less than 100 nanometers in depth stayed free of the particles. In the viral DNA trials, the genetic material appeared as coiled in the deeper channels and elongated in the shallower ones. These results show that the 3-D nanofluidic device successfully excluded rigid nanoparticles based on size and deformed (uncoiled) the flexible DNA strands into distinct shapes at different steps of the staircase.
Currently, the researchers are working to separate and measure mixtures of different-sized nanoparticles and investigate the behavior of DNA captured in a 3-D nanofluidic environment.
In a previous project, the NIST-Cornell researchers used heated air to create nanochannels with curving funnel-shaped entrances in a process they dubbed "nanoglassblowing." Like its new 3-D cousin, the nanoglassblown nanofluidic device facilitates the study of individual DNA strands. More information on nanoglassblowing may be found in the June 10, 2008, issue of NIST Tech Beat at www.nist.gov/public_affairs/techbeat/tb2008_0610.htm#glass.
The work described in the Nanotechnology paper was supported in part by the National Research Council Research Associateship Program and Cornell's Nanobiotechnology Center, part of the National Science Foundation's Science and Technology Center Program. The 3-D nanofluidic devices were fabricated at the Cornell Nanoscale Science and Technology Facility and the Cornell Center for Materials Research, and characterized at the NIST Center for Nanoscale Science and Technology. All experiments were performed at the NIST laboratories in Maryland.
As a non-regulatory agency, NIST promotes U.S. innovation and industrial competitiveness by advancing measurement science, standards and technology in ways that enhance economic security and improve our quality of life.
Stavis, E.A. Strychalski and M.Gaitan. Nanofluidic structures with complex three-dimensional surfaces. Nanotechnology Vol. 20, Issue 16 (online March 31, 2009; in print April 22, 2009).
####
About NIST
NIST's mission:
To promote U.S. innovation and industrial competitiveness by advancing measurement science, standards, and technology in ways that enhance economic security and improve our quality of life.
NIST's vision:
NIST will be the world’s leader in creating critical measurement solutions and promoting equitable standards. Our efforts stimulate innovation, foster industrial competitiveness, and improve the quality of life.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Michael E. Newman
NIST
(301) 975-3025
Copyright © NIST
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Nanoelectronics
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
![]() Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
![]() Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








