Home > Press > Nature, nanotechnology fuse in electric yarn that detects blood
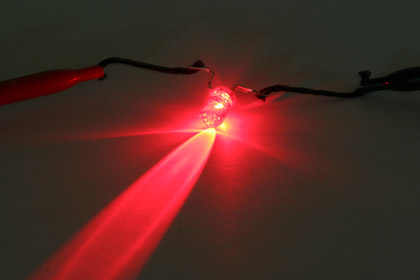 |
| This carbon-nanotube coated smart yarn can conduct enough electricity from a battery to power a light-emitting diode device. Researchers can use its conductivity to design garments that detect blood. |
Abstract:
A carbon nanotube-coated "smart yarn" that conducts electricity could be woven into soft fabrics that detect blood and monitor health, engineers at the University of Michigan have demonstrated.
Nature, nanotechnology fuse in electric yarn that detects blood
ANN ARBOR, MI | Posted on December 15th, 2008"Currently, smart textiles are made primarily of metallic or optical fibers. They're fragile. They're not comfortable. Metal fibers also corrode. There are problems with washing such electronic textiles. We have found a much simpler way---an elegant way---by combining two fibers, one natural and one created by nanotechnology," said Nicholas Kotov, a professor in the departments of Chemical Engineering, Materials Science and Engineering and Biomedical Engineering.
Kotov and Bongsup Shim, a doctoral student in the Department of Chemical Engineering, are among the co-authors of a paper on this material currently published online in Nano Letters.
To make these "e-textiles," the researchers dipped 1.5-millimeter thick cotton yarn into a solution of carbon nanotubes in water and then into a solution of a special sticky polymer in ethanol. After being dipped just a few times into both solutions and dried, the yarn was able to conduct enough power from a battery to illuminate a light-emitting diode device.
"This turns out to be very easy to do," Kotov said. "After just a few repetitions of the process, this normal cotton becomes a conductive material because carbon nanotubes are conductive."
The only perceptible change to the yarn is that it turned black, due to the carbon. It remained pliable and soft.
In order to put this conductivity to use, the researchers added the antibody anti-albumin to the carbon nanotube solution. Anti-albumin reacts with albumin, a protein found in blood. When the researchers exposed their anti-albumin-infused smart yarn to albumin, they found that the conductivity significantly increased. Their new material is more sensitive and selective as well as more simple and durable than other electronic textiles, Kotov said.
Clothing that can detect blood could be useful in high-risk professions, the researchers say. An unconscious firefighter, ambushed soldier, or police officer in an accident, for example, couldn't send a distress signal to a central command post. But the smart clothing would have this capability.
Kotov says a communication device such as a mobile phone could conceivably transmit information from the clothing to a central command post.
"The concept of electrically sensitive clothing made of carbon-nanotube-coated cotton is flexible in implementations and can be adapted for a variety of health monitoring tasks as well as high performance garments," Kotov said.
It is conceivable that clothes made out of this material could be designed to harvest energy or store it, providing power for small electronic devices, but such developments are many years away and pose difficult challenges, the engineers say.
The paper published online in Nano Letters is titled, "Smart Electronic Yarns and Wearable Fabrics for Human Biomonitoring Made by Carbon Nanotube Coating with Polyelectrolytes." Other contributors are with Jiangnan University in China.
This research was funded by the National Science Foundation, the Office of Naval Research, the Air Force Office of Scientific Research and the National Natural Science Foundation of China.
For more information: Nicholas Kotov: www.engin.umich.edu/dept/cheme/people/kotov.html
####
About University of Michigan
The University of Michigan College of Engineering is ranked among the top engineering schools in the country. At more than $130 million annually, its engineering research budget is one of largest of any public university. Michigan Engineering is home to 11 academic departments and a National Science Foundation Engineering Research Center. The college plays a leading role in the Michigan Memorial Phoenix Energy Institute and hosts the world class Lurie Nanofabrication Facility. For more information, visit: www.engin.umich.edu.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Nicole Casal Moore
734-647-1838
Copyright © University of Michigan
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanotubes/Buckyballs/Fullerenes/Nanorods/Nanostrings/Nanosheets
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
Textiles/Clothing
![]() Protective equipment with graphene nanotubes meets the strictest ESD safety standards March 25th, 2022
Protective equipment with graphene nanotubes meets the strictest ESD safety standards March 25th, 2022
![]() Polymer fibers with graphene nanotubes make it possible to heat hard-to-reach, complex-shaped items February 11th, 2022
Polymer fibers with graphene nanotubes make it possible to heat hard-to-reach, complex-shaped items February 11th, 2022
![]() Flexible material shows potential for use in fabrics to heat, cool July 3rd, 2020
Flexible material shows potential for use in fabrics to heat, cool July 3rd, 2020
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








