Home > Press > Charcoal a weapon to fight superoxide-induced disease, injury: Nanomaterials soak up radicals, could aid treatment of COVID-19
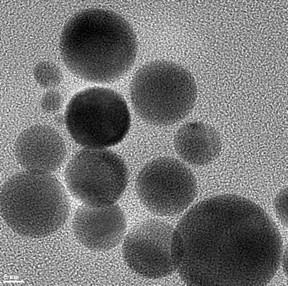 |
| Artificial enzymes made of treated charcoal, seen in this atomic force microscope image, could have the power to curtail damaging levels of superoxides, toxic radical oxygen ions that appear at high concentrations after an injury. (Credit: Tour Group/Rice University) |
Abstract:
Artificial enzymes made of treated charcoal could have the power to curtail damaging levels of superoxides, radical oxygen ions that are toxic at high concentrations.
Charcoal a weapon to fight superoxide-induced disease, injury: Nanomaterials soak up radicals, could aid treatment of COVID-19
Houston, TX | Posted on July 2nd, 2020The nanozymes developed by a Texas Medical Center team are highly effective antioxidants that break down damaging reactive oxygen species (ROS) produced in abundance in response to an injury or stroke.
The researchers suggested the materials, described in the American Chemical Society journal ACS Applied Nano Materials, could aid treatment of COVID-19 patients.
The biocompatible, highly soluble charcoal is a superoxide dismutase, and was synthesized and tested by scientists at Rice University, the University of Texas Health Science Center’s McGovern Medical School and the Texas A&M Health Science Center.
Superoxide dismutases, or SODs, dismantle ROS into ordinary molecular oxygen and hydrogen peroxide. In the project co-led by Rice chemist James Tour, previous materials were successfully tested for their ability to activate the process, including graphene quantum dots drawn from coal and polyethylene glycol-hydrophilic carbon clusters made from carbon nanotubes.
They have now found oxidized charcoal nanoparticles are not only effective antioxidants but can also be made from an activated carbon source that is inexpensive, good manufacturing practice (GMP)-certified and already being used in humans to treat acute poisoning.
“That these nanozymes are made from a GMP source opens the door for drug manufacturers,” said Tour, who led the project with A&M neurologist Thomas Kent and UTHealth biochemist Ah-Lim Tsai. “While coal was effective, an issue is that it can have a variety of toxic metallic elements and impurities that are not consistent across samples. And the clusters made from carbon nanotubes are very expensive.”
The disclike nanozymes are prepared from powdered, medical-grade charcoal oxidized by treatment with highly concentrated nitric acid. The nanozymes teem with oxygen-containing functional groups that bust up superoxides in solution.
Tour noted the nanozymes are able to pass through the membranes of cells’ mitochondria to quench a major source of free radicals without killing the cells themselves. “We published a paper on this recently,” he said. “This seems to be really important to why these work so well in traumatic brain injury and stroke.”
The researchers noted it may be worthwhile to study the application of their nanozymes to treat the cytokine storms -- an excessive immune system response to infection -- suspected of contributing to tissue and organ damage in COVID-19 patients.
“While speculative that these particles will be helpful in COVID-19, if administration is timed correctly, they could reduce the damaging radicals that accompany the cytokine storm and could be further chemically modified to reduce other injury-causing features of this disease,” Kent said.
Gang Wu, an assistant professor of hematology at McGovern, and Rice graduate student Emily McHugh are co-lead authors of the study. Co-authors are Vladimir Berka, a senior research scientist at McGovern; Rice graduate students Weiyin Chen, Zhe Wang and Jacob Beckham; Rice undergraduate Trenton Roy; and Paul Derry, an assistant professor at Texas A&M’s Institute of Biosciences and Technology.
Tour is the T.T. and W.F. Chao Chair in Chemistry as well as a professor of computer science and of materials science and nanoengineering at Rice. Kent is the Robert A. Welch Chair Professor in the Institute of Biosciences and Technology at Texas A&M-Houston Campus and an adjunct chemistry professor at Rice and at Houston Methodist Hospital. Tsai is a professor of hematology at UTHealth.
The National Institutes of Health and the Welch Foundation supported the research.
####
About Rice University
Located on a 300-acre forested campus in Houston, Rice University is consistently ranked among the nation’s top 20 universities by U.S. News & World Report. Rice has highly respected schools of Architecture, Business, Continuing Studies, Engineering, Humanities, Music, Natural Sciences and Social Sciences and is home to the Baker Institute for Public Policy. With 3,962 undergraduates and 3,027 graduate students, Rice’s undergraduate student-to-faculty ratio is just under 6-to-1. Its residential college system builds close-knit communities and lifelong friendships, just one reason why Rice is ranked No. 1 for lots of race/class interaction and No. 4 for quality of life by the Princeton Review. Rice is also rated as a best value among private universities by Kiplinger’s Personal Finance.
Follow Rice News and Media Relations via Twitter @RiceUNews.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Jeff Falk
713-348-6775
Mike Williams
713-348-6728
Copyright © Rice University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() Coal could yield treatment for traumatic injuries:
Coal could yield treatment for traumatic injuries:
![]() Nano-antioxidants prove their potential:
Nano-antioxidants prove their potential:
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
Quantum Dots/Rods
![]() A new kind of magnetism November 17th, 2023
A new kind of magnetism November 17th, 2023
![]() IOP Publishing celebrates World Quantum Day with the announcement of a special quantum collection and the winners of two prestigious quantum awards April 14th, 2023
IOP Publishing celebrates World Quantum Day with the announcement of a special quantum collection and the winners of two prestigious quantum awards April 14th, 2023
![]() Qubits on strong stimulants: Researchers find ways to improve the storage time of quantum information in a spin rich material January 27th, 2023
Qubits on strong stimulants: Researchers find ways to improve the storage time of quantum information in a spin rich material January 27th, 2023
![]() NIST’s grid of quantum islands could reveal secrets for powerful technologies November 18th, 2022
NIST’s grid of quantum islands could reveal secrets for powerful technologies November 18th, 2022
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








