Home > Press > Extremely low thermal conductivity in 1D soft chain structure BiSeX (X = Br, I)
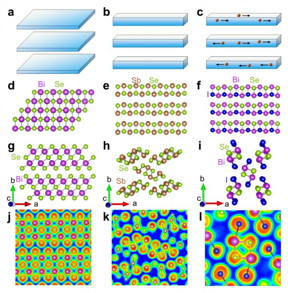 |
| Schematic crystal structures and electronic localization functions (ELFs) of 2D, 1D, and soft 1D Bi2Se3, Sb2Se3 and BiSeI, respectively. Schematic diagrams and corresponding crystal structures of (a, d) 2D slabs in Bi2Se3, (b, e) 1D chain in Sb2Se3 and (c, f) 1D chain with migration of halogens in BiSeI. The crystal structures of Bi2Se3, Sb2Se3and BiSeI viewed along the c direction are given in (g-i), respectively. (j-l) The projected ELF along the chain. The isosurface level of ELF is 0.9. CREDIT ©Science China Press |
Abstract:
The low thermal transport properties are important for applications in thermoelectrics and thermal barrier coatings. Nowadays, the strategies to acquire low thermal conductivity in bulk materials include multi-scale defect (atomic, nano- and meso-scale), heavy molecular weight, complex crystal structure, larger unit cell and strong anharmonicity.
Extremely low thermal conductivity in 1D soft chain structure BiSeX (X = Br, I)
Beijing, China | Posted on June 19th, 2020In a recent article in Science China Materials, Prof. Li-Dong Zhao from Beihang University and co-workers proposed a new strategy to search intrinsically low thermal conductivity in one-dimensional crystal structure. By using the first-principles calculations and experimental synthesis, they found a sort of material with extremely low thermal conductivity, namely BiSeX (X= Br, I) with one-dimensional chain structure. The mechanisms behind the low thermal conductivity were revealed from the aspect of crystal structure, by neutron powder-diffraction measurements and temperature tunable aberration-corrected scanning transmission electron microscopy (STEM).
To elucidate the origins of ultralow thermal conductivity, the authors make comparisons with several analogues that exhibit cubic- (3D), layer- (2D) and chain-like (1D) crystal structures and find that the thermal conductivity shows a decreasing trend from 3D, 2D to 1D (Fig. 1), which is due to the chemical bonding strength between the low-dimensional structure becoming progressively weaker and weaker.
"Based on these guidelines, we found that the chemical bonding along the chain further weakened with added halogen atom", said Prof. Zhao. Therefore, the chemical bondings of BiSeX along all three crystallographic directions are weaker than in other compounds (Fig. 2), showing a quasi-0D crystal structure.
Different from the ultrahigh thermal conductivity diamond (> 2000 W m-1 K-1) with strong covalent bond between carbon atoms, the phonon transport in bismuth selenohalides was significantly suppressed. As a result, they exhibit extremely low thermal conductivity. "The thermal conductivity of BiSeI at 573 K reaches ~0.27 W m-1 K-1, which is close to the theoretical minimum value", emphasized by Prof. Zhao.
These findings open up a prospect of achieving low thermal conductivity materials in one-dimensional chain-containing bulk structure with potential applications in the fields of thermal barrier coatings, thermoelectric materials, etc.
###
This work was published online in Science China Materials and highlighted by Science (Science, 368 (2020) 1325.) (Fig. 3).
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2018YFA0702100, 2018YFB0703600), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51772012, 51632005), the National Science Foundation for Distinguished Young Scholars (51925101), Shenzhen Peacock Plan team (KQTD2016022619565991), Beijing Natural Science Foundation (JQ18004), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation Grant (2019M650429) and 111 Project (B17002).
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Li-Dong Zhao
Copyright © Science China Press
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
Thin films
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








