Home > Press > CEA-Leti Researchers Break Throughput Record for LiFi Communications Using Single GaN Blue Micro-Light-Emitting Diode: Data-Transmission Rate of 7.7 Gbps Positions LiFi as Possible Replacement for WiFi with Further R&D and Industrial Standardization to Ensure Interoperability of
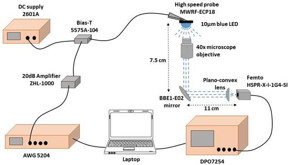 |
| CEA-Leti testbed for single GaN blue microLED that achieved throughput of 7.7 Gbps |
Abstract:
CEA-Leti today announced its researchers have broken the throughput world record of 5.1 Gbps in visible light communications (VLC) using a single GaN blue micro- light-emitting diode (LED). Their data transmission rate of 7.7 Gbps achieved with a 10 µm microLED marks another step toward commercialization and widespread use of LiFi communication.
CEA-Leti Researchers Break Throughput Record for LiFi Communications Using Single GaN Blue Micro-Light-Emitting Diode: Data-Transmission Rate of 7.7 Gbps Positions LiFi as Possible Replacement for WiFi with Further R&D and Industrial Standardization to Ensure Interoperability of
Grenoble, France | Posted on June 12th, 2020VLC, commonly called LiFi (short for “light fidelity”), is an emerging wireless communication system that offers an alternative or a complementary technology to radio frequency (RF) systems such as WiFi and 5G. It is considered to be a promising technology for security-related applications because light propagation can be confined to a room with no information leakage, as opposed to WiFi communication, which penetrates walls. LiFi also holds promise for ultra-highspeed data transmission in environments where RF emissions are controlled, like hospitals, schools, and airplanes.
Single microLED communications offer an ultra-high data-transmission rate for a variety of opportunities for new applications. These include industrial wireless high-speed links in demanding environments such as assembly lines and data centers, and contact-less connectors, or chip-to-chip communication. But their weak optical power limits their applications to short-range communications. In contrast, matrices of thousands of microLEDs contain higher optical powers than open mid- and long-range applications. However, preserving the bandwidth of each microLED within a matrix requires that each signal has to be brought as close as possible to the micro-optical source.
‘Exciting Potential for Mass-Market Applications’
CEA-Leti’s expertise in the microLED epitaxial process produces microLEDs as small as 10 microns, which is among the smallest in the world. The smaller the emissive area of the LED, the higher the communication bandwidth – 1.8 GHz in the institute’s single-blue microLED project. The team also produced an advanced multi-carrier modulation combined with digital signal processing. This high-spectrum-efficiency waveform was transmitted by the single LED and was received on a high-speed photodetector and demodulated using a direct sampling oscilloscope.
“This technology has exciting potential for mass-market applications,” said Benoit Miscopein, CEA-Leti research scientist. “Multi-LED systems could replace WiFi, but wide-scale adoption will require a standardization process to ensure the systems’ interoperability between different manufacturers. The Light Communications Alliance was created in 2019 to encourage the industry to implement this standardization.”
In addition to a stand-alone WiFi-like standard, the possibility to include this new technology as a component carrier in the downlink of 5G-NR, a radio-access technology for 5G mobile considerations, is also under investigation to bring a large additional license-free bandwidth.
“This may be feasible because CEA-Leti’s LiFi physical layer relies on the same concepts as WiFi and 5G technologies,” said Miscopein. “Matrices of thousands of microLEDs could also open the way to mid- to long-range applications, such as indoor wireless multiple access.”
Preserving the bandwidth of each microLED within a matrix requires that each signal is generated as close as possible to the micro-optical source.
“To meet this challenge, we expect to hybridize the microLED matrix onto another matrix of CMOS drivers: one simple CMOS driver will pilot one microLED,” Miscopein said. “This will also enable the additional feature of piloting each microLED pixel independently, and that allows new types of digital-to-optical waveforms that could eliminate the need for digital-to-analog converters commonly used in the conventional ‘analogue’ implementations of LiFi.”
While the Light Communications Alliance will promote interoperability between different manufacturers’ LiFi systems, CEA-Leti will continue its research in two areas:
§ A better understanding of the electrical behavior of single LEDs in high frequency regimes and the link between bandwidth and electromigration patterns, and
§ Techniques to improve the range and/or increase the data rate using multi-LED emissive devices. This requires adapting the waveform generation as well as a CMOS interposer to drive the matrix on a pixel basis.
####
About CEA Leti
Leti, a technology research institute at CEA, is a global leader in miniaturization technologies enabling smart, energy-efficient and secure solutions for industry. Founded in 1967, CEA-Leti pioneers micro-& nanotechnologies, tailoring differentiating applicative solutions for global companies, SMEs and startups. CEA-Leti tackles critical challenges in healthcare, energy and digital migration. From sensors to data processing and computing solutions, CEA-Leti’s multidisciplinary teams deliver solid expertise, leveraging world-class pre-industrialization facilities. With a staff of more than 1,900, a portfolio of 3,100 patents, 10,000 sq. meters of cleanroom space and a clear IP policy, the institute is based in Grenoble, France, and has offices in Silicon Valley and Tokyo. CEA-Leti has launched 65 startups and is a member of the Carnot Institutes network. Follow us on www.leti-cea.com and @CEA_Leti.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Press Contact
Agency
+33 6 74 93 23 47
Copyright © CEA Leti
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Wireless/telecommunications/RF/Antennas/Microwaves
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








