Home > Press > Armored with plastic 'hair' and silica, new perovskite nanocrystals show more durability
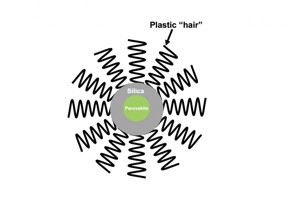 |
| This illustration shows how the two layers of plastic and silica work together to protect the perovskite material. CREDIT Georgia Tech |
Abstract:
Perovskite nanocrystals hold promise for improving a wide variety of optoelectronic devices - from lasers to light emitting diodes (LEDs) - but problems with their durability still limit the material's broad commercial use.
Armored with plastic 'hair' and silica, new perovskite nanocrystals show more durability
Atlanta, GA | Posted on November 29th, 2019Researchers at the Georgia Institute of Technology have demonstrated a novel approach aimed at addressing the material's durability problem: encasing the perovskite inside a double-layer protection system made from plastic and silica.
In a study published Nov. 29 in the journal Science Advances, the research team describes a multistep process to produce encased perovskite nanocrystals that exhibit strong resistance to degradation in moist environments.
"Perovskite nanocrystals are highly susceptible to degradation, particularly when they come into contact with water," said Zhiqun Lin, a professor in the Georgia Tech School of Materials Science and Engineering. "This dual-shelled system offers two layers of protection while allowing each nanocrystal to remain a distinct and separate unit, achieving the maximum amount of surface area and other physical characteristics of the perovskite needed for optimizing optoelectronic applications."
The term perovskite refers to the crystal structure of the material, which is generally composed of three parts: two cations of different sizes and an anion in between. For decades, researchers have tested substituting various chemicals into the structure to achieve unique characteristics. In particular, perovskites containing halide compounds such as bromide and iodine can act as light absorbers and emitters.
For this study, which was supported by the Air Force Office of Scientific Research, the National Science Foundation, the Defense Threat Reduction Agency, and the Department of Energy, Lin's group worked with one of the most common halide configurations, which is formed from methylammonium, lead, and bromide.
Their process involves first forming star-shaped plastic molecules that could serve as "nanoreactors" by growing 21 polymer arms on a simple sugar molecule. Then, once precursor chemicals for the silica and perovskite nanocrystals are loaded onto the plastic molecule, several stages of chemical reactions produce the final system.
After the star-shaped plastic has played its role as a nanoreactor, the star-shaped components remain permanently attached, almost like hair, to the silica, which encases the perovskite. The hairs then serve as the first layer of protection, repelling water and preventing the nanocrystals from clumping together. The subsequent layer of silica adds further protection should any water get past the water-repelling plastic hair.
"Synthesis and applications of perovskite nanocrystals have been a rapidly evolving research field over the past five years," said Yanjie He, a coauthor of the paper and former graduate student at Georgia Tech. "Our strategy, based on a judiciously designed star-shaped plastic as a nanoreactor, enables unprecedented control in the crafting of high-quality perovskite nanocrystals with complex architecture, which is inaccessible in conventional approaches."
To test the material, the researchers coated glass substrates with a thin film of the encapsulated perovskites and conducted several stress tests, including immersing the entire sample in deionized water. By shining ultraviolet light upon the sample, they found that the photoluminescent properties of the perovskites never diminished during a 30-minute test. For comparison, the researchers also immersed unencapsulated perovskites in water and watched as their photoluminescence vanished in a matter of seconds.
Lin said the new method unlocks the possibility of tuning the surface characteristics of the dual-shelled nanocrystal to enhance its performance in a greater range of applications. The process of fabricating the new perovskite nanocrystals from the star-shaped plastic was also unique in that it employed low-boiling point solvents with low toxicity. Future research may center on developing different perovskite nanocrystal systems, including all-inorganic perovskites, double perovskites, and doped perovskites.
"We envision that this type of perovskite nanocrystal will prove very useful for creating durable optoelectronic devices for bioimaging, biosensors, photonic sensors, and radiation detection, as well as next generation LEDs, lasers, and scintillators," Lin said. "This is because these hairy perovskite nanocrystals carry unique advantages, including high defect tolerance, narrower emission bands, and high scintillation efficiency."
###
This research was supported by the National Science Foundation (NSF) under grant Nos. CMMI 1727313, CMMI 1914713, CBET 1803495, Air Force Office of Scientific Research under grant No. FA9550-19-1-0317, the Defense Threat Reduction Agency under grant No. HDTRA1-18-1-0004, and the U.S. Department of Energy under grant Nos. DE-SC0018611 and DE-FG02-90ER46604. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the sponsoring organizations.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Josh Brown
404-385-0500
@GeorgiaTech
Copyright © Georgia Institute of Technology
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Display technology/LEDs/SS Lighting/OLEDs
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Perovskites
![]() KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Optical computing/Photonic computing
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
![]() Nanophotonic platform boosts efficiency of nonlinear-optical quantum teleportation April 25th, 2025
Nanophotonic platform boosts efficiency of nonlinear-optical quantum teleportation April 25th, 2025
![]() Groundbreaking research unveils unified theory for optical singularities in photonic microstructures December 13th, 2024
Groundbreaking research unveils unified theory for optical singularities in photonic microstructures December 13th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








