Home > Press > Researchers reach milestone in use of nanoparticles to kill cancer with heat
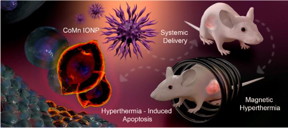 |
| Graphic depiction of the process of using cobalt- and manganese-doped nanoparticles to kill tumors via magnetic hyperthermia. CREDIT Tetiana Korzun |
Abstract:
Researchers at Oregon State University have developed an improved technique for using magnetic nanoclusters to kill hard-to-reach tumors.
Researchers reach milestone in use of nanoparticles to kill cancer with heat
Corvallis, OR | Posted on June 28th, 2019Magnetic nanoparticles - tiny pieces of matter as small as one-billionth of a meter - have shown anti-cancer promise for tumors easily accessible by syringe, allowing the particles to be injected directly into the cancerous growth.
Once injected into the tumor, the nanoparticles are exposed to an alternating magnetic field, or AMF. This field causes the nanoparticles to reach temperatures in excess of 100 degrees Fahrenheit, which causes the cancer cells to die.
But for some cancer types such as prostate cancer, or the ovarian cancer used in the Oregon State study, direct injection is difficult. In those types of cases, a "systemic" delivery method - intravenous injection, or injection into the abdominal cavity - would be easier and more effective.
The challenge for researchers has been finding the right kind of nanoparticles - ones that, when administered systemically in clinically appropriate doses, accumulate in the tumor well enough to allow the AMF to heat cancer cells to death.
Olena Taratula and Oleh Taratula of the OSU College of Pharmacy tackled the problem by developing nanoclusters, multiatom collections of nanoparticles, with enhanced heating efficiency. The nanoclusters are hexagon-shaped iron oxide nanoparticles doped with cobalt and manganese and loaded into biodegradable nanocarriers.
Findings were published in ACS Nano.
"There had been many attempts to develop nanoparticles that could be administered systemically in safe doses and still allow for hot enough temperatures inside the tumor," said Olena Taratula, associate professor of pharmaceutical sciences. "Our new nanoplatform is a milestone for treating difficult-to-access tumors with magnetic hyperthermia. This is a proof of concept, and the nanoclusters could potentially be optimized for even greater heating efficiency."
The nanoclusters' ability to reach therapeutically relevant temperatures in tumors following a single, low-dose IV injection opens the door to exploiting the full potential of magnetic hyperthermia in treating cancer, either by itself or with other therapies, she added.
"It's already been shown that magnetic hyperthermia at moderate temperatures increases the susceptibility of cancer cells to chemotherapy, radiation and immunotherapy," Taratula said.
The mouse model in this research involved animals receiving IV nanocluster injections after ovarian tumors had been grafted underneath their skin.
"To advance this technology, future studies need to use orthotopic animal models - models where deep-seated tumors are studied in the location they would actually occur in the body," she said. "In addition, to minimize the heating of healthy tissue, current AMF systems need to be optimized, or new ones developed."
###
The National Institutes of Health, the OSU College of Pharmacy and Najran University of Saudi Arabia supported this research.
Also collaborating were OSU electrical engineering professor Pallavi Dhagat, postdoctoral scholars Xiaoning Li and Canan Schumann of the College of Pharmacy, pharmacy graduate students Hassan Albarqi, Fahad Sabei and Abraham Moses, engineering graduate student Mikkel Hansen, and pre-pharmacy undergrads Tetiana Korzun and Leon Wong.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Olena Taratula
862-368-4602
Copyright © Oregon State University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Cancer
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








