Home > Press > Nanobody inhibits metastasis of breast tumor cells to lung in mice: “In the present study we describe the development of an inhibitory nanobody directed against an extracellular epitope present in the native V-ATPase c subunit.”
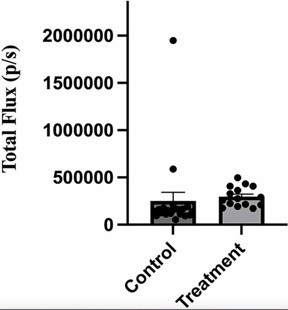 |
| Figure 6: Administration of anti-V-ATPase nanobody does not affect intensity of leg metastases in mice receiving implanted 4T1-12B cells. 20 BALB/c mice were implanted with 4T1-12B cells in the mammary fat pad and then received injections of 66 μg of nanobody in PBS (or PBS alone for control mice) IP three times per week for 3 weeks. Prior to sacrifice mice were injected IP with luciferin and hind legs were removed and imaged ex vivo using a Perkin Elmer IVIS SpectrumCT In Vivo Imaging System. The intensity of the luminescence signal was quantitated using the Living Image® software. Credit 2024 Li et al. |
Abstract:
August 15, 2024 – A new research paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 15 on August 14, 2024, entitled, “A nanobody against the V-ATPase c subunit inhibits metastasis of 4T1-12B breast tumor cells to lung in mice.”
Nanobody inhibits metastasis of breast tumor cells to lung in mice: “In the present study we describe the development of an inhibitory nanobody directed against an extracellular epitope present in the native V-ATPase c subunit.”
Buffalo, NY | Posted on August 16th, 2024The vacuolar H+-ATPase (V-ATPase) is an ATP-dependent proton pump that functions to control the pH of intracellular compartments as well as to transport protons across the plasma membrane of various cell types, including cancer cells.
Researchers Zhen Li, Mohammed A. Alshagawi, Rebecca A. Oot, Mariam K. Alamoudi, Kevin Su, Wenhui Li, Michael P. Collins, Stephan Wilkens, and Michael Forgac from Tufts University School of Medicine; Tufts University; Dana Farber Cancer Institute, Harvard Medical School; University of Minnesota School of Medicine; Prince Sattam Bin Abdulaziz University; Korro Bio; SUNY Upstate Medical University; and Foghorn Therapeutics, have previously shown that selective inhibition of plasma membrane V-ATPases in breast tumor cells inhibits the invasion of these cells in vitro. They have now developed a nanobody directed against an extracellular epitope of the mouse V-ATPase c subunit.
“We show that treatment of 4T1-12B mouse breast cancer cells with this nanobody inhibits V-ATPase-dependent acidification of the media and invasion of these cells in vitro.”
The research team further found that injecting this nanobody into mice implanted with 4T1-12B cells orthotopically in the mammary fat pad inhibited the metastasis of tumor cells to the lungs.
“In conclusion, our results indicate that a nanobody directed against an extracellular epitope expressed on the surface of the V-ATPase is able to inhibit activity of cell surface V-ATPases in 4T1-12B breast cancer cells, inhibit in vitro invasion of these cells and inhibit metastasis of these cells to lung following their implantation in the mammary fat pad of mice.”
####
About Impact Journals LLC
About Oncotarget:
Oncotarget (a primarily oncology-focused, peer-reviewed, open access journal) aims to maximize research impact through insightful peer-review; eliminate borders between specialties by linking different fields of oncology, cancer research and biomedical sciences; and foster application of basic and clinical science.
Oncotarget is indexed and archived by PubMed/Medline, PubMed Central, Scopus, EMBASE, META (Chan Zuckerberg Initiative) (2018-2022), and Dimensions (Digital Science).
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Ryan Braithwaite
Impact Journals LLC
Copyright © Impact Journals LLC
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Closing the gaps — MXene-coating filters can enhance performance and reusability February 28th, 2025
Closing the gaps — MXene-coating filters can enhance performance and reusability February 28th, 2025
![]() Rice researchers harness gravity to create low-cost device for rapid cell analysis February 28th, 2025
Rice researchers harness gravity to create low-cost device for rapid cell analysis February 28th, 2025
Cancer
![]() The mechanism of a novel circular RNA circZFR that promotes colorectal cancer progression July 5th, 2024
The mechanism of a novel circular RNA circZFR that promotes colorectal cancer progression July 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Closing the gaps — MXene-coating filters can enhance performance and reusability February 28th, 2025
Closing the gaps — MXene-coating filters can enhance performance and reusability February 28th, 2025
![]() Rice researchers harness gravity to create low-cost device for rapid cell analysis February 28th, 2025
Rice researchers harness gravity to create low-cost device for rapid cell analysis February 28th, 2025
Nanomedicine
![]() Multiphoton polymerization: A promising technology for precision medicine February 28th, 2025
Multiphoton polymerization: A promising technology for precision medicine February 28th, 2025
![]() Rice researchers harness gravity to create low-cost device for rapid cell analysis February 28th, 2025
Rice researchers harness gravity to create low-cost device for rapid cell analysis February 28th, 2025
![]() SMART researchers pioneer first-of-its-kind nanosensor for real-time iron detection in plants February 28th, 2025
SMART researchers pioneer first-of-its-kind nanosensor for real-time iron detection in plants February 28th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() Closing the gaps — MXene-coating filters can enhance performance and reusability February 28th, 2025
Closing the gaps — MXene-coating filters can enhance performance and reusability February 28th, 2025
![]() Rice researchers harness gravity to create low-cost device for rapid cell analysis February 28th, 2025
Rice researchers harness gravity to create low-cost device for rapid cell analysis February 28th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Closing the gaps — MXene-coating filters can enhance performance and reusability February 28th, 2025
Closing the gaps — MXene-coating filters can enhance performance and reusability February 28th, 2025
![]() Rice researchers harness gravity to create low-cost device for rapid cell analysis February 28th, 2025
Rice researchers harness gravity to create low-cost device for rapid cell analysis February 28th, 2025
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Leading the charge to better batteries February 28th, 2025
Leading the charge to better batteries February 28th, 2025
![]() Quantum interference in molecule-surface collisions February 28th, 2025
Quantum interference in molecule-surface collisions February 28th, 2025
![]() New ocelot chip makes strides in quantum computing: Based on "cat qubits," the technology provides a new way to reduce quantum errors February 28th, 2025
New ocelot chip makes strides in quantum computing: Based on "cat qubits," the technology provides a new way to reduce quantum errors February 28th, 2025
Nanobiotechnology
![]() Multiphoton polymerization: A promising technology for precision medicine February 28th, 2025
Multiphoton polymerization: A promising technology for precision medicine February 28th, 2025
![]() Rice researchers harness gravity to create low-cost device for rapid cell analysis February 28th, 2025
Rice researchers harness gravity to create low-cost device for rapid cell analysis February 28th, 2025
![]() SMART researchers pioneer first-of-its-kind nanosensor for real-time iron detection in plants February 28th, 2025
SMART researchers pioneer first-of-its-kind nanosensor for real-time iron detection in plants February 28th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








