Home > Press > Good vibrations: Using piezoelectricity to ensure hydrogen sensor sensitivity
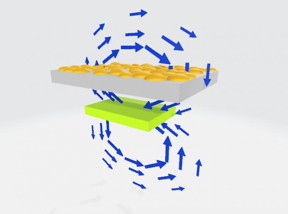 |
| Illustration of how piezoelectric resonance can be used to evaluate the separation between the palladium particles during device fabrication. As palladium nanoparticles (yellow) are being added to the sample, the vibrating piezoelectric material (green rectangular parallelepiped) generates an alternating electric field (blue arrows) near the substrate (gray) surface, creating a current flow in deposited palladium (orange particles). This causes some of the vibrational energy of the piezoelectric material to be lost. The value of the energy loss is greatest when the palladium particles contact each other, so deposition can be stopped at the optimal nanoparticle concentration. CREDIT Osaka University |
Abstract:
Researchers at Osaka University develop a new process for producing palladium nanoparticles that are 12 times more sensitive to hydrogen than those made with previous methods -- devices that may be vital to the transition to a hydrogen energy ecosystem.
Good vibrations: Using piezoelectricity to ensure hydrogen sensor sensitivity
Osaka, Japan | Posted on May 24th, 2019 A team at Osaka University has invented a new process for creating high-precision sensing devices that respond to the presence of hydrogen gas. By carefully controlling the deposition of metallic nanoparticles on a silicon surface, the researchers were able to create a sensor that can detect low levels of hydrogen on the basis of changes in electrical current. This research may have important benefits as part of a switch to hydrogen-based fuels, which could power the zero-emission cars of the future and help fight anthropogenic climate change.
To fabricate a hydrogen sensor, the researchers deposited metallic palladium on a silicon substrate. The deposited palladium forms nanoparticles on the substrate, and they act like tiny islands that are excellent conductors of electricity, but, because they do not form a connected network, the current across the device is very small.
However, when hydrogen atoms are present, they are absorbed into the palladium nanoparticles, increasing volume of the nanoparticles, and then bridge the gaps between the islands. Eventually, a completely connected path is formed, and electrons can flow with much less resistance. In this way, even a tiny change in hydrogen concentration can lead to a massive increase in current, so the devices can be made very sensitive.
A significant challenge the Osaka researchers had to overcome was precisely controlling the gaps between islands to deposit in the first place. If the deposition time was too short, gaps between the nanoparticles are too wide and they would not be bridged even when hydrogen was present. Conversely, if the deposition time was too long, the nanoparticles would form a connected network on their own, even before hydrogen was applied. To optimize the response of the sensor, the research team developed a novel method for monitoring and controlling the deposition of palladium called piezoelectric resonance.
"Piezoelectric materials, such as a quartz crystal in a wristwatch, can vibrate at a very specific frequency in response to an applied voltage," senior author Dr. Hirotsugu Ogi explains. Here, a piece of piezoelectric lithium niobate was set to vibrate underneath the sample during the metallic nanoparticle deposition. The oscillating piezoelectric created an electric field around the sample, which in turn induced a current in the device that depended on the connectivity of the palladium network.
Then, the attenuation of the oscillation changes depending on the connectivity. Therefore, by listening to the sound (measuring the attenuation) of the piezoelectric material, the connectivity can be monitored.
"By optimizing the deposition time using the piezoelectric resonance method, the resulting hydrogen sensors were 12 times more sensitive than before," first author Dr. Nobutomo Nakamura says. "These devices may represent a step towards a cleaner energy future involving hydrogen."
####
About Osaka University
Osaka University was founded in 1931 as one of the seven imperial universities of Japan and now has expanded to one of Japan's leading comprehensive universities. The University has now embarked on open research revolution from a position as Japan's most innovative university and among the most innovative institutions in the world according to Reuters 2015 Top 100 Innovative Universities and the Nature Index Innovation 2017. The university's ability to innovate from the stage of fundamental research through the creation of useful technology with economic impact stems from its broad disciplinary spectrum.
Website: https://resou.osaka-u.ac.jp/en/top
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Saori Obayashi
81-661-055-886
Copyright © Osaka University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Environment
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Automotive/Transportation
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








