Home > Press > Spintronics 'miracle material' put to the test: Physicists build devices using mineral perovskite
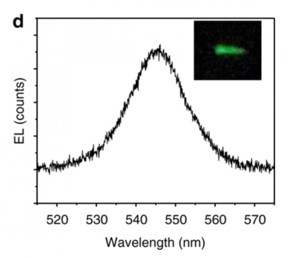 |
| These are the wavelengths of light emitted from the spintronic LED. The inset shows the green light from the device. CREDIT University of Utah |
Abstract:
When German mineralogist Gustav Rose stood on the slopes of Russia's Ural Mountains in 1839 and picked up a piece of a previously undiscovered mineral, he had never heard of transistors or diodes or had any concept of how conventional electronics would become an integral part of our daily lives. He couldn't have anticipated that the rock he held in his hand, which he named "perovskite," could be a key to revolutionizing electronics as we know them.
Spintronics 'miracle material' put to the test: Physicists build devices using mineral perovskite
Salt Lake City, UT | Posted on January 11th, 2019In 2017, University of Utah physicist Valy Vardeny called perovskite a "miracle material" for an emerging field of next-generation electronics, called spintronics, and he's standing by that assertion. In a paper published today in Nature Communications, Vardeny, along with Jingying Wang, Dali Sun (now at North Carolina State University) and colleagues present two devices built using perovskite to demonstrate the material's potential in spintronic systems. Its properties, Vardeny says, bring the dream of a spintronic transistor one step closer to reality.
Spintronics
A conventional digital electronic system conveys a binary signal (think 1s and 0s) through pulses of electrons carried through a conductive wire. Spintronics can convey additional information via another characteristic of electrons, their spin direction (think up or down). Spin is related to magnetism. So spintronics uses magnetism to align electrons of a certain spin, or "inject" spin into a system.
If you've ever done the old science experiment of turning a nail into a magnet by repeatedly dragging a magnet along its length, then you've already dabbled in spintronics. The magnet transfers information to the nail. The trick is then transporting and manipulating that information, which requires devices and materials with finely tuned properties. Researchers are working toward the milestone of a spin transistor, a spintronics version of the electronic components found in practically all modern electronics. Such a device requires a semiconductor material in which a magnetic field can easily manipulate the direction of electrons' spin--a property called spin-orbit coupling. It's not easy to build such a transistor, Wang says. "We keep searching for new materials to see if they're more suitable for this purpose."
Here's where perovskites come into play.
Perovskites
Perovskites are a class of mineral with a particular atomic structure. Their value as a technological material has only became apparent in the past 10 years. Because of that atomic structure, researchers have been developing perovskite into a material for making solar panels. By 2018 they'd achieved an efficiency of up to 23 percent of solar energy converted to electrical energy--a big step up from 3.8 percent in 2009.
In the meantime, Vardeny and his colleagues were exploring the possibilities of spintronics and the various materials that could prove effective in transmitting spin. Because of heavy lead atoms in perovskite, physicists predicted that the mineral may possess strong spin-orbit coupling. In a 2017 paper, Vardeny and physics assistant professor Sarah Li showed that a class of perovskites called organic-inorganic hybrid perovskites do indeed possess large spin-orbit coupling. Also, the lifetime of spin injected into the hybrid materials lasted a relatively long time. Both results suggested that this kind of hybrid perovskite held promise as a spintronics material.
Two spintronic devices
The next step, which Vardeny and Wang accomplished in their recent work, was to incorporate hybrid perovskite into spintronic devices. The first device is a spintronic light-emitting diode, or LED. The semiconductor in a traditional LED contains electrons and holes--places in atoms where electrons should be, but aren't. When electrons flow through the diode, they fill the holes and emit light.
Wang says that a spintronic LED works much the same way, but with a magnetic electrode, and with electron holes polarized to accommodate electrons of a certain spin. The LED lit up with circularly polarized electroluminescence, Wang says, showing that the magnetic electrode successfully transferred spin-polarized electrons into the material.
"It's not self-evident that if you put a semiconductor and a ferromagnet together you get a spin injection," Vardeny adds. "You have to prove it. And they proved it."
The second device is a spin valve. Similar devices already exist and are used in devices such as computer hard drives. In a spin valve, an external magnetic field flips the polarity of magnetic materials in the valve between an open, low-resistance state and a closed, high-resistance state.
Wang and Vardeny's spin valve does more. With hybrid perovskite as the device material, the researchers can inject spin into the device and then cause the spin to precess, or wobble, within the device using magnetic manipulation.
That's a big deal, the researchers say. "You can develop spintronics that are not only useful for recording information and data storage, but also calculation," Wang says. "That was an initial goal for the people who started the field of spintronics, and that's what we are still working on."
Taken together, these experiments show that perovskite works as a spintronic semiconductor. The ultimate goal of a spin-based transistor is still several steps away, but this study lays important groundwork for the path ahead.
"What we've done is to prove that what people thought was possible with perovskite actually happens," Vardeny says. "That's a big step."
###
This work was funded by the U.S. Department of Energy Office of Science.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Paul Gabrielsen
801-505-8253
Copyright © University of Utah
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() The full study can be found here:
The full study can be found here:
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Perovskites
![]() KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
![]() Efficient and stable hybrid perovskite-organic light-emitting diodes with external quantum efficiency exceeding 40 per cent July 5th, 2024
Efficient and stable hybrid perovskite-organic light-emitting diodes with external quantum efficiency exceeding 40 per cent July 5th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Spintronics
![]() Quantum materials: Electron spin measured for the first time June 9th, 2023
Quantum materials: Electron spin measured for the first time June 9th, 2023
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Quantum Computing
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Quantum nanoscience
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








