Home > Press > Unraveling the mystery of how black widow spiders create steel-strength silk webs: ‘Modified micelle theory’ may allow scientists to create equally strong synthetic materials
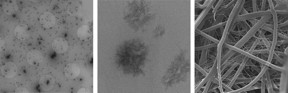 |
| Utilizing state-of-the-art techniques — nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, the same technology utilized in MRI, at SDSU, followed by electron microscopy at Northwestern — the research team was able to more closely see inside the protein gland where the silk fibers originate, revealing a much more complex, hierarchical protein assembly. (Photo credit: SDSU) |
Abstract:
Researchers at Northwestern University and San Diego State University (SDSU) have better unraveled the complex process of how black widow spiders transform proteins into steel-strength fibers. This knowledge promises to aid scientists in creating equally strong synthetic materials.
Unraveling the mystery of how black widow spiders create steel-strength silk webs: ‘Modified micelle theory’ may allow scientists to create equally strong synthetic materials
Evanston, IL | Posted on October 23rd, 2018Black widow spiders and their relatives, native to temperate climates in North America, Europe, Asia, Australia, Africa and South America, produce an array of silks with exceptional materials properties.
Scientists have long known the primary sequence of amino acids that make up some spider silk proteins and understood the structure of the fibers and webs. Previous research theorized that spider silk proteins await the spinning process as nano-size amphiphilic spherical micelles (clusters of water soluble and non-soluble molecules) before being funneled through the spider’s spinning apparatus to form silk fibers. However, when scientists attempted to replicate this process, they were unable to create synthetic materials with the strengths and properties of native spider silk fibers.
“The knowledge gap was literally in the middle,” Northwestern’s Nathan C. Gianneschi said. “What we didn’t understand completely is what goes on at the nanoscale in the silk glands or the spinning duct — the storage, transformation and transportation process involved in proteins becoming fibers.”
Gianneschi is the Jacob and Rosaline Cohn Professor in the department of chemistry in the Weinberg College of Arts and Sciences and in the departments of materials science and engineering and of biomedical engineering in the McCormick School of Engineering. He and Gregory P. Holland, associate professor in the department of chemistry and biochemistry at SDSU and the author of more than 40 papers on spider silk, are the paper’s co-corresponding authors.
The research was published online on Oct. 22 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS).
Utilizing complementary, state-of-the-art techniques — nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, the same technology utilized in MRI, at SDSU, followed by electron microscopy at Northwestern — the research team was able to more closely see inside the protein gland where the silk fibers originate, revealing a much more complex, hierarchical protein assembly.
This “modified micelles theory” concludes that spider silk proteins do not start out as simple spherical micelles, as previously thought, but instead as complex, compound micelles. This unique structure is potentially required to create the black widow spider’s impressive fibers.
“We now know that black widow spider silks are spun from hierarchical nano-assemblies (200 to 500 nanometers in diameter) of proteins stored in the spider’s abdomen, rather than from a random solution of individual proteins or from simple spherical particles,” Holland said.
If duplicated, “the practical applications for a material like this are essentially limitless,” Holland said, and could include high-performance textiles for military, first responders and athletes; building materials for cable bridges and other construction; environmentally friendly replacements for plastics; and biomedical applications.
“One cannot overstate the potential impact on materials and engineering if we can synthetically replicate this natural process to produce artificial fibers at scale,” said Gianneschi, who also is the associate director of the International Institute for Nanotechnology and a member of the Simpson Querrey Institute and the Chemistry of Life Processes Institute at Northwestern. “Simply put, it would be transformative.”
The study was funded in part by the U.S. Department of Defense through the Air Force Office of Scientific Research and the Army Research Office (ARO).
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Amanda Morris
847-467-6790
Source contacts:
Nathan Gianneschi
and Gregory P. Holland
Copyright © Northwestern University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
Textiles/Clothing
![]() Protective equipment with graphene nanotubes meets the strictest ESD safety standards March 25th, 2022
Protective equipment with graphene nanotubes meets the strictest ESD safety standards March 25th, 2022
![]() Polymer fibers with graphene nanotubes make it possible to heat hard-to-reach, complex-shaped items February 11th, 2022
Polymer fibers with graphene nanotubes make it possible to heat hard-to-reach, complex-shaped items February 11th, 2022
![]() Flexible material shows potential for use in fabrics to heat, cool July 3rd, 2020
Flexible material shows potential for use in fabrics to heat, cool July 3rd, 2020
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








