Home > Press > Extracting energy from a 60 nanometers thin layer
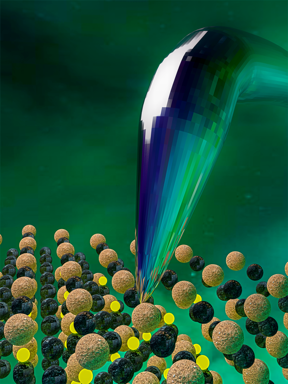 |
| Figure 1: 3D representation of the AFM nanometric tip used to obtain the direct piezoelectric characteristic of a thin film ferroelectric material. The BFO ferroelectric material, with perovskite crystal structure, was used to demonstrate that the direct effect takes a role at the nanoscale level. |
Abstract:
A team of researchers have demonstrated the viability of the direct piezoelectric effect in a thin film Bismuth Ferrite Material for the first time. The work, published in Nanoscale entitles “Direct and Converse Piezoelectric Responses at the Nanoscale from Epitaxial BiFeO3 Thin Films Grown by Polymer Assisted Deposition” which has gained the cover letter of such journal.
Extracting energy from a 60 nanometers thin layer
Bellaterra, Spain | Posted on October 5th, 2018In this particular research, the BFO was scanned in a novel methodology named “Direct Piezoelectric Force Microscopy” DPFM, a new AFM mode invented in 2017
( https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-017-01361-2 ). The material in this mode is stressed by the AFM tip with nanometric size. The tip applies a force in the range of hundreds of microNewton and measures the generated charge that is created by the material. For the case of BFO material, the piezoelectric characteristics were collected when the tip crosses antiparallel domain configurations, see the following video for a 3D representation of the tip crossing such configuration:
https://youtu.be/ir3W2Vk8hCs
The good quality of the films arising from a novel method based in polymer assisted deposition ensured a constant and reliable current signal. Nevertheless the reliability, the signal to measure is, because of the generated charge, extremely weak. Specifically, researcher measured currents in the femtoAmpere level (10E-15 Amperes). Consider that a typical personal computer consumes around 1 A. The current signal was integrated to find the d33 characteristics of the material. This research is crucial for the development of piezoelectric material and it is understanding at the nanoscale, being the very first time that the direct piezoelectric effect also works at the nanoscale.
“More info:
Direct and converse piezoelectric responses at the nanoscale from epitaxial BiFeO3 thin films grown by polymer assisted deposition. Nanoscale (2018) DOI:10.1039/C8NR05737K
Piezo-generated charge mapping revealed through Direct Piezoelectric Force Microscopy, A. Gomez et al. , Nature Communications (2017), DOI: 10.1038/s41467-017-01361-2”
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Andrés Gómez Rodríguez
Scanning Probe Microscopy Laboratory
ICMAB
Campus UAB
08193, Bellaterra
Spain
+(34)935 801 853 Ext. 389
http://services.icmab.es/spm/
Copyright © ICMAB
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
Thin films
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
Videos/Movies
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








