Home > Press > The nanoscience of ferroelectric and ferromagnetic domains converges on Barcelona
 |
Abstract:
The 14th International Symposium of Ferroic Domains is a highly specialised event organised by members of the ICN2 Oxide Nanophysics Group to discuss phenomena with implications for fundamental physics and electronic applications. Find out more here.
The nanoscience of ferroelectric and ferromagnetic domains converges on Barcelona
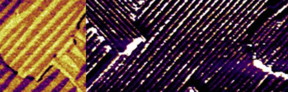
Barcelona, Spain | Posted on September 27th, 2018Ferroelectric and ferromagnetic materials, meaning those with a spontaneous electric or magnetic polarisation, often contain regions of opposite polarity, known as "domains". The increasing precision achieved in the study and manipulation of these jigsaw-like regions has led to the emergence of a whole new area of research with major implications for the design of electronic devices, that of ferroic domains. This week the 14th International Symposium on Ferroic Domains brings nearly a hundred of the world’s top specialists to Barcelona to discuss the latest advances.
Held every two years since 1989, this year the event has been organised by ICREA Prof. Gustau Catalán, leader of the ICN2 Oxide Nanophysics Group, and Dr Neus Domingo, senior researcher in this group and head of the ICN2 Advanced Atomic Force Microscopy Platform. The event has been coordinated from the ICN2, member of the Barcelona Institute of Science and Technology (BIST).
To understand these structures a precision at the nanoscale is required. The domain walls separating areas with opposite properties may be infinitely long, though nanoscopically thin. They may also be straight or they may trace more complex lines, twisting into record-small vortexes or spirals. With an example being skyrmions, despite their small size they are extremely robust. Furthermore, these walls can conduct electricity and be moved around within the material, making it possible to write and delete infinitely many electronic circuits on a single material simply by changing the configuration of its domains.
All of these things are already possible through the use of scanning probe microscopes, which can not only observe, but also manipulate materials at the nanoscale with an unprecedented level of control.
The conference in Barcelona will highlight the latest advances and point the future trends in this very exciting new area of research.
####
For more information, please click here
Copyright © ICN2
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
Magnetism/Magnons
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Events/Classes
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
![]() A New Blue: Mysterious origin of the ribbontail ray’s electric blue spots revealed July 5th, 2024
A New Blue: Mysterious origin of the ribbontail ray’s electric blue spots revealed July 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers demonstrate co-propagation of quantum and classical signals: Study shows that quantum encryption can be implemented in existing fiber networks January 20th, 2023
Researchers demonstrate co-propagation of quantum and classical signals: Study shows that quantum encryption can be implemented in existing fiber networks January 20th, 2023
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








