Home > Press > Magnetic skyrmions: Not the only ones of their class: Jülich researchers discover a new type of magnetic particle-like object for data storage devices of the future
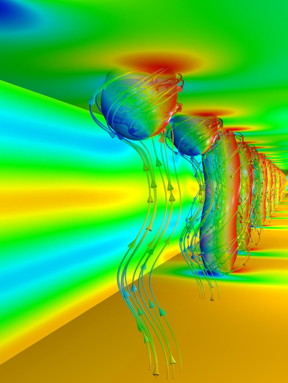 |
| Encoding digital data as a sequence of magnetic bobbers (foreground) and skyrmions (further back). CREDIT Forschungszentrum Jülich/N. Kiselev |
Abstract:
These objects, which are referred to as "chiral magnetic bobbers", are three-dimensional magnetic structures that appear near the surfaces of certain alloys.
Magnetic skyrmions: Not the only ones of their class: Jülich researchers discover a new type of magnetic particle-like object for data storage devices of the future
Juelich, Germany | Posted on June 28th, 2018"For a long time, the unique object for research in the field of chiral magnets was the magnetic skyrmion. We now provide a new object for investigation by researchers - a chiral bobber - which is characterized by a number of unique properties", says Dr. Nikolai Kiselev from Jülich's Peter Grünberg Institute (PGI-1). Three years ago, together with the institute's Director Prof. Stefan Blügel and other collaborators, they predicted the existence of this new class of magnetic structures theoretically. Now, researchers from the Ernst Ruska-Centre for Microscopy and Spectroscopy with Electrons (Director Prof. Rafal E. Dunin-Borkowski and his colleagues) have succeeded in demonstrating the existence of chiral bobbers in a real material experimentally.
The stability of magnetic structures such as skyrmions is related to a property of the material known as chirality. Just as a right hand cannot be converted into a left hand for reasons of symmetry, right-handed and left-handed magnetic structures cannot be converted into one another. Furthermore, both skyrmions and the newly-discovered chiral bobbers are very small, with diameters of typically only a few tens of nanometers. Therefore, they can in principle be used to pack data very densely on a memory chip. However, their small size makes their observation highly challenging. "The visualization of magnetic texture on such a small scale requires special state-of-the-art techniques that are accessible in only a few laboratories worldwide", explains Rafal Dunin-Borkowski.
There is another important reason why magnetic solitons (another name for particle-like objects in nonlinear physics) such as skyrmions and chiral bobbers are so promising for applications. In contrast to data bits in hard disk drives, skyrmions are movable objects. Their motion along a guiding track in a chip can be induced by a very weak pulse of electrical current. This property provides new opportunities for the development of a completely new concept of magnetic solid-state memory - the so-called skyrmion racetrack memory. "The mobility of skyrmions allows data to move from write to read elements without the need for any movable mechanical parts such as read and write heads and spining hard disk itself", explains Nikolai Kiselev. This capability saves energy because components that move generally require more energy, occupy more space and tend to be sensitive to mechanical vibrations and shocks. A new solid state magnetic memory would be free of such disadvantages.
The newly discovered magnetic particles now make it possible to encode digital data directly with two different types of magnetic objects, namely with skyrmions and magnetic bobbers.
"Until now, it was assumed that digital data should somehow be represented as a sequence of skyrmions and empty spaces", says Stefan Blügel. The distance between successive skyrmions then encodes binary information. However, it must then be controlled or quantized, so that no information is lost through spontaneous drift of the skyrmions. Instead, the newly discovered three-dimensional magnetic particles offer opportunities to encode digital data directly as a sequence of skyrmions and magnetic bobbers, which can each flow freely without needing to maintain precise distances between successive data bit carriers.
Further research is required to develop practical applications. In the iron-germanium alloy studied by Nikolai Kiselev and his colleagues, the structures are only stable up to 200 Kelvin, which corresponds to -73.5 degrees Celsius. However, based on theoretical considerations, it is predicted that magnetic bobbers may also occur in other chiral magnets and, like some recently discovered species of skyrmions, may also exist at room temperature.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Tobias Schloesser
49-246-161-4771
Copyright © Forschungszentrum Juelich
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
Magnetism/Magnons
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Skyrmions
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Memory Technology
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








