Home > Press > Camouflaged nanoparticles used to deliver killer protein to cancer
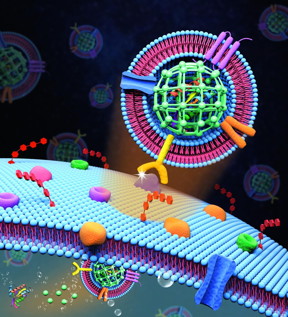 |
| Extracellular vesicle-like metal-organic framework nanoparticles are developed for the intracellular delivery of biofunctional proteins. The biomimetic nanoplatform can protect the protein cargo and overcome various biological barriers to achieve systemic delivery and autonomous release. Credit: Zheng Lab/Penn State CREDIT Zheng Lab/Penn State |
Abstract:
A biomimetic nanosystem can deliver therapeutic proteins to selectively target cancerous tumors, according to a team of Penn State researchers. Using a protein toxin called gelonin from a plant found in the Himalayan mountains, the researchers caged the proteins in self-assembled metal-organic framework (MOF) nanoparticles to protect them from the body's immune system. To enhance the longevity of the drug in the bloodstream and to selectively target the tumor, the team cloaked the MOF in a coating made from cells from the tumor itself.
Camouflaged nanoparticles used to deliver killer protein to cancer
University Park, PA | Posted on June 17th, 2018Blood is a hostile environment for drug delivery. The body's immune system attacks alien molecules or else flushes them out of the body through the spleen or liver. But cells, including cancer cells, release small particles called extracellular vesicles that communicate with other cells in the body and send a "don't eat me" signal to the immune system.
"We designed a strategy to take advantage of the extracellular vesicles derived from tumor cells," said Siyang Zheng, associate professor of biomedical and electrical engineering at Penn State. "We remove 99 percent of the contents of these extracellular vesicles and then use the membrane to wrap our metal-organic framework nanoparticles. If we can get our extracellular vesicles from the patient, through biopsy or surgery, then the nanoparticles will seek out the tumor through a process called homotypic targeting."
Gong Cheng, lead author on a new paper describing the team's work and a former post-doctoral scholar in Zheng's group now at Harvard, said, "MOF is a class of crystalline materials assembled by metal nodes and organic linkers. In our design, self-assembly of MOF nanoparticles and encapsulation of proteins are achieved simultaneously through a one-pot approach in aqueous environment. The enriched metal affinity sites on MOF surfaces act like the buttonhook, so the extracellular vesicle membrane can be easily buckled on the MOF nanoparticles. Our biomimetic strategy makes the synthetic nanoparticles look like extracellular vesicles, but they have the desired cargo inside."
The nanoparticle system circulates in the bloodstream until it finds the tumor and locks on to the cell membrane. The cancer cell ingests the nanoparticle in a process called endocytosis. Once inside the cell, the higher acidity of the cancer cell's intracellular transport vesicles causes the metal-organic framework nanoparticles to break apart and release the toxic protein into cytosol and kill the cell.
"Our metal-organic framework has very high loading capacity, so we don't need to use a lot of the particles and that keeps the general toxicity low," Zheng said.
The researchers studied the effectiveness of the nanosystem and its toxicity in a small animal model and reported their findings in a cover article in the Journal of the American Chemical Society.
The researchers believe their nanosystem provides a tool for the targeted delivery of other proteins that require cloaking from the immune system. Penn State has applied for patent protection for the technology.
###
Besides lead author Gong Cheng and senior author Siyang Zheng, co-authors on the paper, titled "Self-assembly of Extracellular Vesicle-like Metal-Organic Framework Nanoparticle for Protection and Intracellular Delivery of Biofunctional Proteins," are post-doctoral scholars Wenqing Li, Xiaohui Han, Yuan Wan, and Zhigang Wang, graduate students Laura Ha, Sijie Hao and Xin Zou, all in Zheng's group, and associate professor of biology Yingwei Mao and his doctoral student Fengping Dong.
Penn State's Materials Research Institute and Huck Institutes of the Life Sciences, and the National Institutes of Health supported this work.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
A'ndrea Elyse Messer
814-865-9481
Copyright © Penn State
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Cancer
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








