Home > Press > Self-assembling 3D battery would charge in seconds
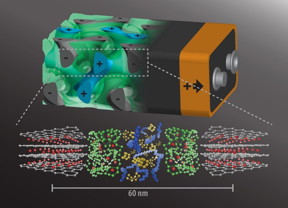 |
| Wiesner Group/Provided A rendering of the 3D battery architecture (top; not to scale) with interpenetrating anode (grey, with minus sign), separator (green), and cathode (blue, plus sign), each about 20 nanometers in size. Below are their respective molecular structures. |
Abstract:
The world is a big place, but it's gotten smaller with the advent of technologies that put people from across the globe in the palm of one's hand. And as the world has shrunk, it has also demanded that things happen ever faster - including the time it takes to charge an electronic device.
Self-assembling 3D battery would charge in seconds
Ithaca, NY | Posted on May 22nd, 2018A cross-campus collaboration led by Ulrich Wiesner, professor of engineering in the at Cornell University, addresses this demand with a novel energy storage device architecture that has the potential for lightning-quick charges.
The group's idea: Instead of having the batteries' anode and cathode on either side of a nonconducting separator, intertwine the components in a self-assembling, 3D gyroidal structure, with thousands of nanoscale pores filled with the elements necessary for energy storage and delivery.
"This is truly a revolutionary battery architecture," said Wiesner, whose group's paper, "Block Copolymer Derived 3-D Interpenetrating Multifunctional Gyroidal Nanohybrid for Electrical Energy Storage," was published May 16 in Energy and Environmental Science, a publication of the Royal Society of Chemistry.
"This three-dimensional architecture basically eliminates all losses from dead volume in your device," Wiesner said. "More importantly, shrinking the dimensions of these interpenetrated domains down to the nanoscale, as we did, gives you orders of magnitude higher power density. In other words, you can access the energy in much shorter times than what's usually done with conventional battery architectures." How fast is that? Wiesner said that, due to the dimensions of the battery's elements being shrunk down to the nanoscale, "by the time you put your cable into the socket, in seconds, perhaps even faster, the battery would be charged."
The architecture for this concept is based on block copolymer self-assembly, which the Wiesner group has employed for years in other devices, including a gyroidal solar cell and a gyroidal superconductor. Joerg Werner, Ph.D. '15, lead author on this work, had experimented with self-assembling photonic devices, and wondered if the same principles could be applied to carbon materials for energy storage.
The gyroidal thin films of carbon - the battery's anode, generated by block copolymer self-assembly - featured thousands of periodic pores on the order of 40 nanometers wide. These pores were then coated with a 10 nm-thick, electronically insulating but ion-conducting separator through electropolymerization, which by the very nature of the process produced a pinhole-free separation layer.
That's vital, since defects like holes in the separator are what can lead to catastrophic failure giving rise to fires in mobile devices such as cellphones and laptops.
The next step is the addition of the cathode material - in this case, sulfur - in an amount that doesn't quite fill the remainder of the pores. Since sulfur can accept electrons but doesn't conduct electricity, the final step is backfilling with an electronically conducting polymer - known as PEDOT (poly[3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene]).
While this architecture offers proof of concept, Wiesner said, it's not without challenges. Volume changes during discharging and charging the battery gradually degrade the PEDOT charge collector, which doesn't experience the volume expansion that sulfur does.
"When the sulfur expands," Wiesner said, "you have these little bits of polymer that get ripped apart, and then it doesn't reconnect when it shrinks again. This means there are pieces of the 3D battery that you then cannot access."
The group is still perfecting the technique, but applied for patent protection on the proof-of-concept work.
###
Other collaborators on this work included Héctor Abruña, the Emile M. Chamot Professor in the Department of Chemistry and Chemical Biology, and G.G. Rodriguez-Calero, Ph.D. '14, formerly of the Abruña group.
This work was supported as part of the Energy Materials Center at Cornell (emc2), funded by the U.S. Department of Energy as well as in part by the National Science Foundation. Experimentation was conducted at the Cornell Center for Materials Research (CCMR) and the Cornell High Energy Synchrotron Source (CHESS), both of which are supported by the NSF.
Cornell University has television, ISDN and dedicated Skype/Google+ Hangout studios available for media interviews. For additional information, see this Cornell Chronicle story.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Jeff Tyson
607-255-7701
Copyright © Cornell University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Self Assembly
![]() Diamond glitter: A play of colors with artificial DNA crystals May 17th, 2024
Diamond glitter: A play of colors with artificial DNA crystals May 17th, 2024
![]() Liquid crystal templated chiral nanomaterials October 14th, 2022
Liquid crystal templated chiral nanomaterials October 14th, 2022
![]() Nanoclusters self-organize into centimeter-scale hierarchical assemblies April 22nd, 2022
Nanoclusters self-organize into centimeter-scale hierarchical assemblies April 22nd, 2022
![]() Atom by atom: building precise smaller nanoparticles with templates March 4th, 2022
Atom by atom: building precise smaller nanoparticles with templates March 4th, 2022
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Patents/IP/Tech Transfer/Licensing
![]() Getting drugs across the blood-brain barrier using nanoparticles March 3rd, 2023
Getting drugs across the blood-brain barrier using nanoparticles March 3rd, 2023
![]() Metasurfaces control polarized light at will: New research unlocks the hidden potential of metasurfaces August 13th, 2021
Metasurfaces control polarized light at will: New research unlocks the hidden potential of metasurfaces August 13th, 2021
![]() Arrowhead Pharmaceuticals Announces Closing of Agreement with Takeda November 27th, 2020
Arrowhead Pharmaceuticals Announces Closing of Agreement with Takeda November 27th, 2020
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








