Home > Press > Mining for gold with a computer: Texas A&M team gleans new insights on key material
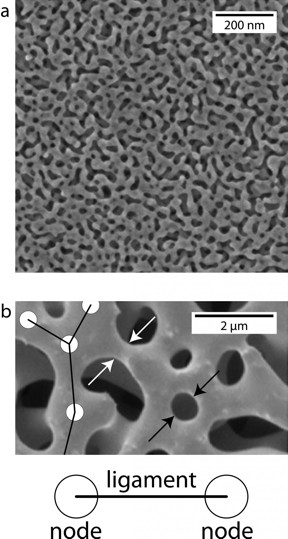 |
| These images show some of the physical characteristics of nanoporous gold at different magnifications. CREDIT Texas A&M University |
Abstract:
Engineers from Texas A&M University and Virginia Tech report important new insights into nanoporous gold--a material with growing applications in several areas, including energy storage and biomedical devices--all without stepping into a lab.
Mining for gold with a computer: Texas A&M team gleans new insights on key material
College Station, TX | Posted on May 3rd, 2018Instead of conducting any additional experiments, the team used image-analysis software developed in-house to "mine" the existing literature on nanoporous gold (NPG). Specifically, the software analyzed photographs of NPG from some 150 peer-reviewed papers, quickly measuring key features of the material that the researchers then correlated with written descriptions of how the samples were prepared. One of the results? A recipe, of sorts, for how to make NPG with specific characteristics.
"We were able to back out a quantitative law that explains how you can change NPG features by changing the processing times and temperatures," said Ian McCue, a postdoctoral researcher in the Texas A&M Department of Materials Science and Engineering. McCue is lead author of a paper on the work published online in the April 30 issue of Scientific Reports.
The team also identified a new parameter related to NPG that could be used to better tune the material for specific applications.
"Before our work, engineers knew of one tunable 'knob' for NPG. Now we have a second one that could give us even more control over the material's properties," said Josh Stuckner, a graduate student at Virginia Tech and co-author of the paper. Stuckner developed the software that allowed the new insights.
Other authors are Dr. Michael J. Demkowicz, associate professor in the materials science and engineering department at Texas A&M, and Dr. Mitsu Murayama, associate professor at Virginia Tech.
Nanoporous gold has been studied for some 15 years, but little is actually known about its physical characteristics and the limits of its tunability for specific applications, the team writes in Scientific Reports.
The material is a three-dimensional porous network of interweaving strands, or ligaments. Multiple ligaments, in turn, connect at points called nodes. All of these features are almost unimaginably small. Stuckner notes, for example, that some of the smaller pores would fit about three strands of DNA side by side. As a result, McCue said the overall structure is very complex and it's been extremely difficult and time-consuming to measure features like the lengths between nodes and the diameters of ligaments. But Stuckner's software has changed that.
"Manually it might take 20 minutes to over an hour to measure the features associated with one image," Stuckner said. "We can do it in a minute, or even just tell the computer to measure a whole slew of images while we walk away."
Earlier attempts to measure NPG features led to very small data sets of five or six data points. The Texas A&M/Virginia Tech team has looked at around 80 data points. That, in turn, allowed the team to create the new quantitative description of NPG features associated with different processing techniques. All that without doing any actual experiments, just clever data-mining and analysis, said McCue.
The work has also led to new publication guidelines for future researchers. Of the 2,000 papers the team originally analyzed, only 150 had useful information.
"We had to throw out a lot of data due to poor image quality or a lack of written information on how a given NPG was processed," McCue said. "The new guidelines could prevent that, ultimately allowing better data mining not only for NPG but for other materials."
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Aubrey Bloom
830-377-8566
Copyright © Texas A&M University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








