Home > Press > Mapping battery materials with atomic precision: Berkeley Lab researchers map the atoms of battery materials and explored how composition affects structure
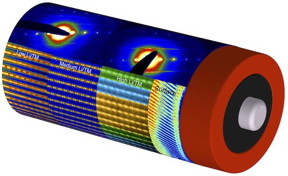 |
| Atomic resolution scanning transmission electron microscopy images and electron diffraction patterns, arranged on a rendering of a battery, show how the structure of lithium-rich and manganese-rich transition metal oxides used inside battery cathodes changes with composition. The images also show how the surface of the cathode has a different structure than the interior. CREDIT Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory |
Abstract:
Lithium-ion batteries are widely used in home electronics and are now being used to power electric vehicles and store energy for the power grid. But their limited number of recharge cycles and tendency to degrade in capacity over their lifetime have spurred a great deal of research into improving the technology.
Mapping battery materials with atomic precision: Berkeley Lab researchers map the atoms of battery materials and explored how composition affects structure
Berkeley, CA | Posted on March 8th, 2018An international team led by researchers from the U.S. Department of Energy's Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) used advanced techniques in electron microscopy to show how the ratio of materials that make up a lithium-ion battery electrode affects its structure at the atomic level, and how the surface is very different from the rest of the material. The work was published in the journal Energy & Environmental Science.
Knowing how the internal and surface structure of a battery material changes over a wide range of chemical compositions will aid future studies on cathode transformations and could also lead to the development of new battery materials.
"This finding could change the way we look at phase transformations within the cathode and the resulting loss of capacity in this class of material," said Alpesh Khushalchand Shukla, a scientist at Berkeley Lab's Molecular Foundry, and lead author of the study. "Our work shows that it is extremely important to completely characterize a new material in its pristine state, as well as after cycling, in order to avoid misinterpretations."
Previous work by researchers at the Molecular Foundry, a research center specializing in nanoscale science, revealed the structure of cathode materials containing "excess" lithium, resolving a longstanding debate.
Using a suite of electron microscopes both at the National Center for Electron Microscopy (NCEM), a Molecular Foundry facility, and at SuperSTEM, the National Research Facility for Advanced Electron Microscopy in Daresbury, U.K., the research team found that while the atoms throughout the interior of the cathode material remained in the same structural pattern across all compositions, decreasing the amount of lithium caused an increase in randomness in the position of certain atoms within the structure.
By comparing different compositions of cathode material to battery performance, the researchers also demonstrated it was possible to optimize battery performance in relation to capacity by using a lower ratio of lithium to other metals.
The most surprising finding was that the surface structure of an unused cathode is very different from the interior of the cathode. A thin layer of material on the surface possessing a different structure, called the "spinel" phase, was found in all of their experiments. Several previous studies had overlooked that this layer might be present on both new and used cathodes.
By systematically varying the ratio of lithium to a transition metal, like trying different amounts of ingredients in a new cookie recipe, the research team was able to study the relationship between the surface and interior structure and to measure the electrochemical performance of the material. The team took images of each batch of the cathode materials from multiple angles and created complete, 3-D renderings of each structure.
"Obtaining such precise, atomic-level information over length scales relevant to battery technologies was a challenge," said Quentin Ramasse, Director of the SuperSTEM Laboratory. "This is a perfect example of why the multiple imaging and spectroscopy techniques available in electron microscopy make it such an indispensable and versatile tool in renewable energy research."
The researchers also used a newly developed technique called 4-D scanning transmission electron microscopy (4-D STEM). In transmission electron microscopy (TEM), images are formed after electrons pass through a thin sample. In conventional scanning transmission electrode microscopy (STEM), the electron beam is focused down to a very small spot (as small as 0.5 nanometers, or billionths of a meter, in diameter) and then that spot is scanned back and forth over the sample like a mower on a lawn.
The detector in conventional STEM simply counts how many electrons are scattered (or not scattered) in each pixel. However, in 4D-STEM, the researchers use a high-speed electron detector to record where each electron scatters, from each scanned point. It allows researchers to measure the local structure of their sample at high resolution over a large field of view.
"The introduction of high-speed electron cameras allows us to extract atomic-scale information from very large sample dimensions," said Colin Ophus, a research scientist at NCEM. "4D-STEM experiments mean we no longer need to make a tradeoff between the smallest features we can resolve and the field-of-view that we are observing - we can analyze the atomic structure of the entire particle at once."
###
Berkeley Lab's Molecular Foundry is a DOE Office of Science User.
This work was supported by the U.S. Department of Energy's Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy, Office of Basic Science, and Small Business Voucher Pilot Program; Envia Systems; and the U.K.'s Engineering and Physical Science Research Council.
####
About Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory
Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory addresses the world's most urgent scientific challenges by advancing sustainable energy, protecting human health, creating new materials, and revealing the origin and fate of the universe. Founded in 1931, Berkeley Lab's scientific expertise has been recognized with 13 Nobel Prizes. The University of California manages Berkeley Lab for the U.S. Department of Energy's Office of Science. For more, visit http://www.lbl.gov .
DOE's Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States, and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, please visit science.energy.gov.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Glenn Roberts Jr.
510-486-5582
Copyright © Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
Laboratories
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Automotive/Transportation
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








