Home > Press > Weak hydrogen bonds key to strong, tough infrastructure: Rice University lab simulates polymer-cement composites to find strongest, toughest materials
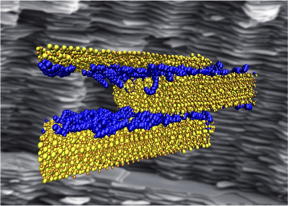 |
| Rice University scientists probing the interfacial interactions of polymer (blue) and cement (yellow) discovered the right mix of hydrogen bonds is critical to making strong, tough and ductile composite materials for infrastructure. Computer simulations like that in the illustration measured the strength of the bonds as hard cement slides past the soft polymer in a layered composite, which mimics the structure nacre, seen in the background. CREDIT Probhas Hundi/Multiscale Materials Laboratory |
Abstract:
The right mix of hydrogen bonds in polymer and cement composites is critical to making strong, tough and ductile infrastructure material, according to Rice University scientists who want to mimic the mechanics of mother-of-pearl and similar natural composites with synthetic materials.
Weak hydrogen bonds key to strong, tough infrastructure: Rice University lab simulates polymer-cement composites to find strongest, toughest materials
Houston, TX | Posted on January 29th, 2018Seashells made of mother-of-pearl, aka nacre, get their remarkable properties from overlapping micron-sized, mineralized plates held together by a soft matrix. This structure can be approached by cement and polymer composites that may, for instance, make better earthquake-resistant concrete, according to Rouzbeh Shahsavari, an assistant professor of civil and environmental engineering.
The Rice lab ran more than 20 computer simulations of how polymers and cement molecules come together at the nanoscale and what drives their adhesion. The researchers showed that the proximity of oxygen and hydrogen atoms is the critical factor in forming a network of weak hydrogen bonds that connects soft and hard layers. Common polyacrylic acid (PAA) proved best at binding the overlapping layers of cement crystals with an optimal overlap of about 15 nanometers.
"This information is important to make the best synthetic composites," said Shahsavari, who ran the project with Rice graduate student Navid Sakhavand. "A modern engineering approach to these materials will have a large impact on society, especially as we build new and replace aging infrastructure."
The lab's results appear in Applied Physics Letters.
While engineers understand that adding polymers improves cement by blocking the damaging effects of "aggressive" ions that invade its pores, details about how the materials interact at the molecular scale have remained unknown, Shahsavari said. To find out, the researchers modeled composites with PAA as well as polyvinyl alcohol (PVA), both soft matrix materials that have been used to improve cement.
They discovered that the two different oxygen atoms in PAA (as opposed to one in PVA) allowed it to receive and donate ions as it bonded with hydrogen in the crystals of tobermorite cement. Oxygen in PAA had eight ways to bond with hydrogen (six for PVA) and could also participate in salt bridging between the polymer and cement, which makes the bonding network even more complex.
The researchers tested their simulated structures by sliding layers of polymer and cement against each other and found that complexity allowed the bonds between PAA and cement to break and reconnect more frequently as the material was stressed, which significantly increases its toughness, the ability to deform without fracturing. This allowed the researchers to determine the optimum overlap between cement crystals.
"In contrast to the common intuition that hydrogen bonds are weak, when the right number of them -- the optimum overlap -- cooperate, they provide sufficient connectivity in the composite to confer high strength and high toughness," Shahsavari said. "From an experimental standpoint, this can be done by carefully tuning and controlling the addition of the polymers with the right molecular weight while controlling cement mineral formation. Indeed, a recent experimental paper by our colleagues showed a proof of concept toward this strategy."
###
The National Science Foundation (NSF) supported the research. Supercomputing resources were supplied by Rice's NSF-supported DAVinCI supercomputer administered by the Center for Research Computing and procured in partnership with Rice's Ken Kennedy Institute for Information Technology.
####
About Rice University
Located on a 300-acre forested campus in Houston, Rice University is consistently ranked among the nation's top 20 universities by U.S. News & World Report. Rice has highly respected schools of Architecture, Business, Continuing Studies, Engineering, Humanities, Music, Natural Sciences and Social Sciences and is home to the Baker Institute for Public Policy. With 3,970 undergraduates and 2,934 graduate students, Rice's undergraduate student-to-faculty ratio is just under 6-to-1. Its residential college system builds close-knit communities and lifelong friendships, just one reason why Rice is ranked No. 1 for quality of life and for lots of race/class interaction and No. 2 for happiest students by the Princeton Review. Rice is also rated as a best value among private universities by Kiplinger's Personal Finance. To read "What they're saying about Rice," go to http://tinyurl.com/RiceUniversityoverview .
Follow Rice News and Media Relations via Twitter @RiceUNews
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
David Ruth
713-348-6327
Copyright © Rice University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() Multiscale Materials Laboratory (Shahsavari Lab):
Multiscale Materials Laboratory (Shahsavari Lab):
![]() George R. Brown School of Engineering:
George R. Brown School of Engineering:
![]() Rice Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering:
Rice Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering:
![]() Rice Department of Materials Science and NanoEngineering:
Rice Department of Materials Science and NanoEngineering:
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Construction
![]() Temperature-sensing building material changes color to save energy January 27th, 2023
Temperature-sensing building material changes color to save energy January 27th, 2023
![]() Strain-sensing smart skin ready to deploy: Nanotube-embedded coating detects threats from wear and tear in large structures July 15th, 2022
Strain-sensing smart skin ready to deploy: Nanotube-embedded coating detects threats from wear and tear in large structures July 15th, 2022
![]() A sunlight-driven “self-healing” anti-corrosion coating May 27th, 2022
A sunlight-driven “self-healing” anti-corrosion coating May 27th, 2022
![]() Polymer fibers with graphene nanotubes make it possible to heat hard-to-reach, complex-shaped items February 11th, 2022
Polymer fibers with graphene nanotubes make it possible to heat hard-to-reach, complex-shaped items February 11th, 2022
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








