Home > Press > 'Nano-hashtags' could provide definite proof of Majorana particles: Eindhoven network of nanowires gives particles the space to exchange places
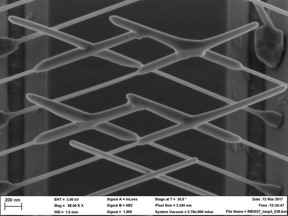 |
| Scanning electron microscope image of growing InP nanowires thereby forming multiple junctions. CREDIT Eindhoven University of Technology |
Abstract:
In Nature today an international team of researchers from Eindhoven University of Technology, Delft University of Technology and the University of California - Santa Barbara presents an advanced quantum chip that will be able to provide definitive proof of the mysterious Majorana particles. These particles, first demonstrated in 2012, are their own antiparticle at one and the same time. The chip, which comprises ultrathin networks of nanowires in the shape of 'hashtags', has all the qualities to allow Majorana particles to exchange places. This feature is regarded as the smoking gun for proving their existence and is a crucial step towards their use as a building block for future quantum computers.
'Nano-hashtags' could provide definite proof of Majorana particles: Eindhoven network of nanowires gives particles the space to exchange places
Eindhoven, The Netherlands | Posted on August 23rd, 2017In 2012 it was big news: researchers from Delft University of Technology and Eindhoven University of Technology presented the first experimental signatures for the existence of the Majorana fermion. This particle had been predicted in 1937 by the Italian physicist Ettore Majorana and has the distinctive property of also being its own anti-particle. The Majorana particles emerge at the ends of a semiconductor wire, when in contact with a superconductor material.
Smoking gun
While the discovered particles may have properties typical to Majoranas, the most exciting proof could be obtained by allowing two Majorana particles to exchange places, or 'braid' as it is scientifically known. "That's the smoking gun," suggests Erik Bakkers, one of the researchers from Eindhoven University of Technology. "The behavior we then see could be the most conclusive evidence yet of Majoranas."
Crossroads
In the Nature paper that is published today, Bakkers and his colleagues present a new device that should be able to show this exchanging of Majoranas. In the original experiment in 2012 two Majorana particles were found in a single wire but they were not able to pass each other without immediately destroying the other. Thus the researchers quite literally had to create space. In the presented experiment they formed intersections using the same kinds of nanowire so that four of these intersections form a 'hashtag', #, and thus create a closed circuit along which Majoranas are able to move.
Etch and grow
The researchers built their hashtag device starting from scratch. The nanowires are grown from a specially etched substrate such that they form exactly the desired network which they then expose to a stream of aluminium particles, creating layers of aluminium, a superconductor, on specific spots on the wires - the contacts where the Majorana particles emerge. Places that lie 'in the shadow' of other wires stay uncovered.
Leap in quality
The entire process happens in a vacuum and at ultra-cold temperature (around -273 degree Celsius). "This ensures very clean, pure contacts," says Bakkers, "and enables us to make a considerable leap in the quality of this kind of quantum device." The measurements demonstrate for a number of electronic and magnetic properties that all the ingredients are present for the Majoranas to braid.
Quantum computers
If the researchers succeed in enabling the Majorana particles to braid, they will at once have killed two birds with one stone. Given their robustness, Majoranas are regarded as the ideal building block for future quantum computers that will be able to perform many calculations simultaneously and thus many times faster than current computers. The braiding of two Majorana particles could form the basis for a qubit, the calculation unit of these computers.
Travel around the world
An interesting detail is that the samples have traveled around the world during the fabrication, combining unique and synergetic activities of each research institution. It started in Delft with patterning and etching the substrate, then to Eindhoven for nanowire growth and to Santa Barbara for aluminium contact formation. Finally back to Delft via Eindhoven for the measurements.
###
References
The article in Nature is entitled 'Epitaxy of Advanced Nanowire Quantum Devices'. The authors are (1: Eindhoven University of Technology, 2: TU Delft, 3: University of California - Santa Barbara, 4: TNO, 5: Niels Bohr Institute (Copenhagen), 6: Philips Innovation Services Eindhoven, 7: Microsoft Station-Q Delft):
Sasa Gazibegovich1,2; Diana Car1,2; Hao Zhang2; Stijn Balk2; John Logan3; Michiel de Moor2; Maja Cassidy2; Rudi Schmits4; Di Xu2; Guanzhong Wang2; Peter Krogstrup5; Roy Op het Veld1,2; Kun Zuo2; Yoram Vos2; Jie Shen2; DaniŽl Bouwman2; Borzoyeh Shojaei3; Daniel Pennachio3; Joon Sue Lee3; Petrus van Veldhoven1; Sebastian Koeling1; Marcel Verheijen1,6; Leo Kouwenhoven2,7; Chris Palmstrom3; Erik Bakkers1,2.
The research has been made possible in part by subsidies from the Dutch research funding organizations NWO and Stichting FOM, the European Research Council and Microsoft Station-Q.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Barry van der Meer
31-628-783-207
Copyright © Eindhoven University of Technology
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Quantum Computing
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
Quantum nanoscience
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








