Home > Press > 3-D-printed jars in ball-milling experiments
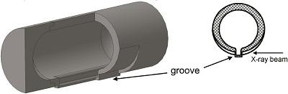 |
| This image shows a thin-walled jar with a groove; isometric view with a cut (left) and cross section (right). CREDIT Tumanov et al |
Abstract:
Mechanochemistry is a widespread synthesis technique in all areas of chemistry. Various materials have been synthesized by this technique when the classical wet chemistry route is not satisfactory. Characterization of the reaction mixture is however much less accessible than in solutions.
3-D-printed jars in ball-milling experiments
Chester, UK | Posted on June 29th, 2017Recently, in situ observations of mechanochemical reactions have been achieved by X-ray diffraction and Raman spectroscopy. Solid-state reactions can be directly tracked, revealing phase transitions and other material transformations during synthesis in a ball mill jar. This technique has become increasingly popular in different fields of mechanochemistry.
As the X-rays go through the entire jar, the diffraction patterns present a high background due to the scattering from the thick walls of the jar. Also, broad diffraction peaks are expected from the sample as a result of probing a large sample area covering the entire jar. An extra complexity arises from diffraction on the milling balls.
Tumanov et al. [(2017). J. Appl. Cryst. 50. doi:10.1107/S1600576717006744] reasoned that these issues can be resolved by modifying the geometry and material of the milling jar. But, making a jar with a complex geometry using traditional production techniques is complicated, especially at the stage of creating a prototype, when introducing changes into a design should be facile. For this reason they decided to use a 3D printer for the purpose. They show how this useful production tool can quickly make milling jars optimized for improved background, absorption and angular resolution in X-ray powder diffraction experiments; the jars are also more resistant to solvents compared with standard acrylic jars. 3D printing allows for low-cost fast production on demand.
Source files for printing the jars are available as supporting information for the paper.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Dr. Jonathan Agbenyega
44-124-434-2878
Copyright © International Union of Crystallography
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
Chemistry
![]() Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
3D & 4D printing/Additive-manufacturing
![]() Presenting: Ultrasound-based printing of 3D materials—potentially inside the body December 8th, 2023
Presenting: Ultrasound-based printing of 3D materials—potentially inside the body December 8th, 2023
![]() Fiber sensing scientists invent 3D printed fiber microprobe for measuring in vivo biomechanical properties of tissue and even single cell February 10th, 2023
Fiber sensing scientists invent 3D printed fiber microprobe for measuring in vivo biomechanical properties of tissue and even single cell February 10th, 2023
![]() 3D-printed decoder, AI-enabled image compression could enable higher-res displays December 9th, 2022
3D-printed decoder, AI-enabled image compression could enable higher-res displays December 9th, 2022
![]() Researchers design new inks for 3D-printable wearable bioelectronics: Potential uses include printing electronic tattoos for medical tracking applications August 19th, 2022
Researchers design new inks for 3D-printable wearable bioelectronics: Potential uses include printing electronic tattoos for medical tracking applications August 19th, 2022
Crystallography
![]() First measurement of electron energy distributions, could enable sustainable energy technologies June 5th, 2020
First measurement of electron energy distributions, could enable sustainable energy technologies June 5th, 2020
![]() How to trick electrons to see the hidden face of crystals: Researchers try a trick for complete 3D analysis of submicron crystals August 3rd, 2019
How to trick electrons to see the hidden face of crystals: Researchers try a trick for complete 3D analysis of submicron crystals August 3rd, 2019
![]() Novel nozzle saves crystals: Double flow concept widens spectrum for protein crystallography March 17th, 2017
Novel nozzle saves crystals: Double flow concept widens spectrum for protein crystallography March 17th, 2017
![]() Nanocages for gold particles: what is happening inside? March 16th, 2017
Nanocages for gold particles: what is happening inside? March 16th, 2017
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Industrial
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() Quantum interference in molecule-surface collisions February 28th, 2025
Quantum interference in molecule-surface collisions February 28th, 2025
![]() Boron nitride nanotube fibers get real: Rice lab creates first heat-tolerant, stable fibers from wet-spinning process June 24th, 2022
Boron nitride nanotube fibers get real: Rice lab creates first heat-tolerant, stable fibers from wet-spinning process June 24th, 2022
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








