Home > Press > Graphene-nanotube hybrid boosts lithium metal batteries: Rice University prototypes store 3 times the energy of lithium-ion batteries
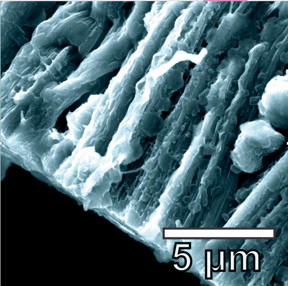 |
| Lithium metal coats the hybrid graphene and carbon nanotube anode in a battery created at Rice University. The lithium metal coats the three-dimensional structure of the anode and avoids forming dendrites. CREDIT Tour Group/Rice University |
Abstract:
Rice University scientists have created a rechargeable lithium metal battery with three times the capacity of commercial lithium-ion batteries by resolving something that has long stumped researchers: the dendrite problem.
Graphene-nanotube hybrid boosts lithium metal batteries: Rice University prototypes store 3 times the energy of lithium-ion batteries
Houston, TX | Posted on May 19th, 2017The Rice battery stores lithium in a unique anode, a seamless hybrid of graphene and carbon nanotubes. The material first created at Rice in 2012 is essentially a three-dimensional carbon surface that provides abundant area for lithium to inhabit.
The anode itself approaches the theoretical maximum for storage of lithium metal while resisting the formation of damaging dendrites or "mossy" deposits.
Dendrites have bedeviled attempts to replace lithium-ion with advanced lithium metal batteries that last longer and charge faster. Dendrites are lithium deposits that grow into the battery's electrolyte. If they bridge the anode and cathode and create a short circuit, the battery may fail, catch fire or even explode.
Rice researchers led by chemist James Tour found that when the new batteries are charged, lithium metal evenly coats the highly conductive carbon hybrid in which nanotubes are covalently bonded to the graphene surface.
As reported in the American Chemical Society journal ACS Nano, the hybrid replaces graphite anodes in common lithium-ion batteries that trade capacity for safety.
"Lithium-ion batteries have changed the world, no doubt," Tour said, "but they're about as good as they're going to get. Your cellphone's battery won't last any longer until new technology comes along."
He said the new anode's nanotube forest, with its low density and high surface area, has plenty of space for lithium particles to slip in and out as the battery charges and discharges. The lithium is evenly distributed, spreading out the current carried by ions in the electrolyte and suppressing the growth of dendrites.
Though the prototype battery's capacity is limited by the cathode, the anode material achieves a lithium storage capacity of 3,351 milliamp hours per gram, close to the theoretical maximum and 10 times that of lithium-ion batteries, Tour said. Because of the low density of the nanotube carpet, the ability of lithium to coat all the way down to the substrate ensures maximum use of the available volume, he said.
The researchers had their "Aha!" moment in 2014, when co-lead author Abdul-Rahman Raji, a former graduate student in Tour's lab and now a postdoctoral researcher at the University of Cambridge, began experimenting with lithium metal and the graphene-nanotube hybrid.
"I reasoned that lithium metal must have plated on the electrode while analyzing results of experiments carried out to store lithium ions in the anode material combined with a lithium cobalt oxide cathode in a full cell," Raji said. "We were excited because the voltage profile of the full cell was very flat. At that moment, we knew we had found something special."
Within a week, Raji and co-lead author Rodrigo Villegas Salvatierra, a Rice postdoctoral researcher, deposited lithium metal into a standalone hybrid anode so they could have a closer look with a microscope. "We were stunned to find no dendrites grown, and the rest is history," Raji said.
To test the anode, the Rice lab built full batteries with sulfur-based cathodes that retained 80 percent capacity after more than 500 charge-discharge cycles, approximately two years' worth of use for a normal cellphone user, Tour said. Electron microscope images of the anodes after testing showed no sign of dendrites or the moss-like structures that have been observed on flat anodes. To the naked eye, anodes within the quarter-sized batteries were dark when empty of lithium metal and silver when full, the researchers reported.
"Many people doing battery research only make the anode, because to do the whole package is much harder," Tour said. "We had to develop a commensurate cathode technology based upon sulfur to accommodate these ultrahigh-capacity lithium anodes in first-generation systems. We're producing these full batteries, cathode plus anode, on a pilot scale, and they're being tested."
###
Co-authors of the paper are Rice postdoctoral researcher Nam Dong Kim, visiting researchers Xiujun Fan and Junwei Sha and graduate students Yilun Li and Gladys López-Silva. Tour is the T.T. and W.F. Chao Chair in Chemistry as well as a professor of computer science and of materials science and nanoengineering at Rice.
The Air Force Office of Scientific Research Multidisciplinary University Research Initiative supported the research.
####
About Rice University
Located on a 300-acre forested campus in Houston, Rice University is consistently ranked among the nation's top 20 universities by U.S. News & World Report. Rice has highly respected schools of Architecture, Business, Continuing Studies, Engineering, Humanities, Music, Natural Sciences and Social Sciences and is home to the Baker Institute for Public Policy. With 3,879 undergraduates and 2,861 graduate students, Rice's undergraduate student-to-faculty ratio is 6-to-1. Its residential college system builds close-knit communities and lifelong friendships, just one reason why Rice is ranked No. 1 for happiest students and for lots of race/class interaction by the Princeton Review. Rice is also rated as a best value among private universities by Kiplinger's Personal Finance. To read "What they're saying about Rice," go to http://tinyurl.com/RiceUniversityoverview .
Follow Rice News and Media Relations via Twitter @RiceUNews
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
David Ruth
713-348-6327
Copyright © Rice University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() Wiess School of Natural Sciences:
Wiess School of Natural Sciences:
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








