Home > Press > Information storage with a nanoscale twist: Discovery of a novel rotational force inside magnetic vortices makes it easier to design ultrahigh capacity disk drives
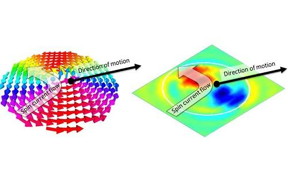 |
| The torque needed to manipulate nanoscale magnetic whirlpools, represented here as red and blue regions with opposite signs, have now been revealed with high-powered synchrotron light. CREDIT Reproduced with permission of 2016 American Physical Society |
Abstract:
Swirling objects known as magnetic vortices and skyrmions can be miniaturized without sacrificing mobility, a KAUST-led international research team has found. These findings are relevant for future "race-track" memory technologies that feature massive densities of moveable magnetic bits1.
Information storage with a nanoscale twist: Discovery of a novel rotational force inside magnetic vortices makes it easier to design ultrahigh capacity disk drives
Thuwal, Saudi Arabia | Posted on March 28th, 2017In nanometer-thin magnetic films, such as iron-nickel alloys, the region separating two magnetic domains or defects can adopt tiny whirlpool-like patterns. Some of these patterns, called skyrmions, resist unraveling even when packed tightly together, and they can also be directed with small electric currents. These features have made the skyrmions attractive targets for research into high-capacity memory devices. One concept zips skyrmions around a loop then past a stationary read/write head to eliminate the need for mechanical components used in today's hard drives.
Aurelien Manchon, an Associate Professor of Material Science and Engineering at the University, notes that one of the main reasons for the appeal of skyrmions is their ability to avoid defects or uneven patches in thin films that would normally trap or "pin" a magnetic charge. However, this agility is compromised when researchers try to shrink skyrmions to the smallest size possible--the smaller they get the more likely they are to get pinned because of the relative increase in defect site dimensions.
To improve these devices, Manchon and international collaborators tried to understand the fundamental momentum transfer between charge currents and magnetic whirlpools.
Using intense x-rays generated at Berkeley University's Advanced Light Source, the team captured time-resolved images of whirlpool patterns called magnetic vortices as they gyrated along a nanometer-wide half-ring track. By pinpointing the position of the vortex core from the imaging sequence, they obtained accurate data about a parameter, known as the non-adiabatic spin-transfer torque, which is crucial for electrical manipulations.
Surprisingly, the measured non-adiabatic torque was far greater than values predicted by existing models. To account for this discrepancy, a theoretical analysis by Manchon showed the extra twisting was provided by another force--the emergent Hall effect, which occurs when electrons travel through a magnetic whirlpool.
"In a nutshell, electrons experience a force that pushes them sideways, but it doesn't come from the local magnetization itself; instead it arises from the topology of the magnetic texture," explained Manchon. "This effect produces an extra spin-polarized current that exerts a torque on the whirlpool."
The researchers found that the additional non-adiabatic torque intensifies when the size of the whirlpool is reduced--a driving force that may offer a way to overcome defect pinning at the nanoscale. "This might be an interesting compromise to seek, especially in the context of skyrmion-based data storage," added Manchon.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Michelle D'Antoni
Copyright © King Abdullah University of Science and Technology
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Skyrmions
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Scientists use heat to create transformations between skyrmions and antiskyrmions January 12th, 2024
Scientists use heat to create transformations between skyrmions and antiskyrmions January 12th, 2024
![]() Spin photonics to move forward with new anapole probe November 4th, 2022
Spin photonics to move forward with new anapole probe November 4th, 2022
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Memory Technology
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








