Home > Press > New optical nanosensor improves brain mapping accuracy, opens way for more applications: Potassium-sensitive fluorescence-imaging method shines light on chemical activity within the brain
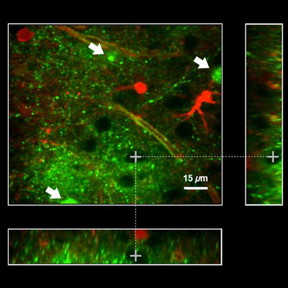 |
| A new optical nanosensor enables more accurate brain mapping and opens the way for broader applications in future; Fig. 5 in a paper reporting on the work shows retention of a potassium nanosensor in the extracellular space. doi:10.1117/1.NPh.4.1.015002 CREDIT The authors |
Abstract:
A new optical nanosensor enabling more accurate measurement and spatiotemporal mapping of the brain also shows the way forward for design of future multimodal sensors and a broader range of applications, say researchers in an article published in the current issue of Neurophotonics. The journal is published by SPIE, the international society for optics and photonics.
New optical nanosensor improves brain mapping accuracy, opens way for more applications: Potassium-sensitive fluorescence-imaging method shines light on chemical activity within the brain
Bellingham, WA and Cardiff, UK | Posted on March 3rd, 2017Neuronal activity results in the release of ionized potassium into extracellular space. Under active physiological and pathological conditions, elevated levels of potassium need to be quickly regulated to enable subsequent activity. This involves diffusion of potassium across extracellular space as well as re-uptake by neurons and astrocytes.
Measuring levels of potassium released during neural activity has involved potassium-sensitive microelectrodes, and to date has provided only single-point measurement and undefined spatial resolution in the extracellular space.
With a fluorescence-imaging-based ionized-potassium-sensitive nanosensor design, a research team from the University of Lausanne was able to overcome challenges such as sensitivity to small movements or drift and diffusion of dyes within the studied region, improving accuracy and enabling access to previously inaccessible areas of the brain.
The work by Joel Wellbourne-Wood, Theresa Rimmele, and Jean-Yves Chatton is reported in "Imaging extracellular potassium dynamics in brain tissue using a potassium-sensitive nanosensor." The article is freely available for download.
"This is a technological breakthrough that promises to shed new light -- both literally and figuratively -- on understanding brain homeostasis," said Neurophotonics associate editor George Augustine, of Duke University. "It not only is much less invasive than previous methods, but it adds a crucial spatial dimension to studies of the role of potassium ions in brain function."
This potassium-sensitive nanosensor is likely to aid future investigations of chemical mechanisms and their interactions within the brain, the authors note. The spatiotemporal imaging created by collected data will also allow for investigation into the possible existence of potassium micro-domains around activated neurons and the spatial extent of these domains. The study confirms the practicality of the nanosensor for imaging in the extracellular space, and also highlights the range of possible extensions and applications of the nanosensor strategy.
###
David Boas of Massachusetts General Hospital, Harvard Medical School, is the editor-in-chief of Neurophotonics. Launched in 2014, Neurophotonics is published digitally in the SPIE Digital Library and in print. The journal covers advances in optical technology applicable to the study of the brain and their impact on basic and clinical neuroscience applications.
The SPIE Digital Library contains more than 458,000 articles from SPIE journals, proceedings, and books, with approximately 18,000 new research papers added each year. Abstracts are freely searchable, and a number of journal articles are published with open access.
####
About SPIE - InternationalSociety for Optics and Photonics
SPIE, the international society for optics and photonics, is an educational not-for-profit organization founded in 1955 to advance light-based science, engineering and technology. The Society serves nearly 264,000 constituents from approximately 166 countries, offering conferences and their published proceedings, continuing education, books, journals, and the SPIE Digital Library. In 2016, SPIE provided $4 million in support of education and outreach programs.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Amy Nelson
360-685-5478
Copyright © SPIE - InternationalSociety for Optics and Photonics
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








