Home > Press > New material with ferroelectricity and ferromagnetism may lead to better computer memory
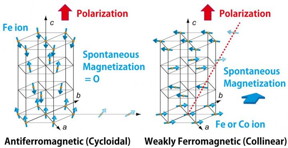 |
| Portions of the BiFeO3 lattice of cycloidal and collinear phases with only Fe ions are shown at left and right, respectively. The arrows indicate the Fe3+ moment direction. The ground state of BiFeO3 had a cycloidal spin structure, which is destabilized by substitution of Co for Fe and at higher temperatures. The spin magnetic moments compensate with each other in the left panel, but canting between neighboring spins leads to the appearance of weak ferromagnetism in the left panel. CREDIT Tokyo Institute of Technology |
Abstract:
Traditional computer memory, known as DRAM, uses electric fields to store information. In DRAM, the presence or absence of an electric charge is indicated either by number 1 or number 0. Unfortunately, this type of information storage is transient and information is lost when the computer is turned off. Newer types of memory, MRAM and FRAM, use long-lasting ferromagnetism and ferroelectricity to store information. However, no technology thus far combines the two.
New material with ferroelectricity and ferromagnetism may lead to better computer memory
Tokyo, Japan | Posted on December 21st, 2016To address this challenge, a group of scientists led by Prof. Masaki Azuma from the Laboratory for Materials and Structures at Tokyo Institute of Technology, along with associate Prof. Hajime Hojo at Kyushu University previously at Tokyo Tech, Prof. Ko Mibu at Nagoya Institute of Technology and five other researchers demonstrated the multiferroic nature of a thin film of BiFe1?xCoxO3 (BFCO). Multiferroic materials exhibit both ferromagnetism and ferroelectricity. These are expected to be used as multiple-state memory devices. Furthermore, if the two orders are strongly coupled and the magnetization can be reversed by applying an external electric field, the material should work as a form of low power consumption magnetic memory.
Previous scientists had speculated that ferroelectric BFO thin film, a close relative of BFCO, might be ferromagnetic as well, but they were thwarted by the presence of magnetic impurity. Prof. M. Azuma's team successfully synthesized pure, thin films of BFCO by using pulsed laser deposition to perform epitaxial growth on a SrTiO3 (STO) substrate. They then conducted a series of tests to show that BFCO is both ferroelectric and ferromagnetic at room temperature. They manipulated the direction of ferroelectric polarization by applying an electric field, and showed that the low-temperature cychloidal spin structure, essentially the same as that of BiFeO3, changes to a collinear one with ferromagnetism at room temperature.
In the future, the scientists hope to realize electrical control of ferromagnetism, which could be applied in low power consumption, non-volatile memory devices.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Emiko Kawaguchi
81-357-342-975
Copyright © Tokyo Institute of Technology
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
Magnetism/Magnons
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Thin films
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Memory Technology
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








