Home > Press > Imec and Holst Centre Introduce World’s First Solid-State Multi-Ion Sensor for Internet-of-Things Applications
 |
Abstract:
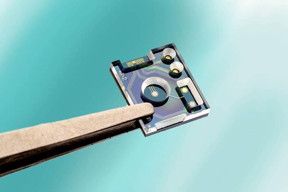
At last week’s IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM) in San Francisco (USA), imec, the world-leading research and innovation hub in nano-electronics and digital technology and Holst Centre debuted a miniaturized sensor that simultaneously determines pH and chloride (Cl-)levels in fluid. This innovation is a must have for accurate long-term measurement of ion concentrations in applications such as environmental monitoring, precision agriculture and diagnostics for personalized healthcare. The sensor is an industry first and thanks to the SoC (system on chip) integration it enables massive and cost-effective deployments in Internet-of-Things (IoT) settings. Its innovative electrode design results in a similar or better performance compared to today’s standard equipment for measuring single ion concentrations and allows for additional ion tests.
Imec and Holst Centre Introduce World’s First Solid-State Multi-Ion Sensor for Internet-of-Things Applications
Leuven, Belgium | Posted on December 13th, 2016Sensors based on ion-selective membranes are considered the gold standard to measure ion concentrations in many applications, such as water quality, agriculture, and analytical chemistry. They consist of two electrodes, the ion-sensitive electrode with the membrane (ISE) and a reference electrode (RE). When these electrodes are immersed in a fluid, a potential is generated that scales with the logarithm of the ion activity in the fluid, forming a measure for the concentration. However, the precision of the sensor depends on the long-term stability of the miniaturized RE, a challenge that has now been overcome.
“The common issue with such designs is the leaching of ions from the internal electrolyte, causing the sensor to drift over time,” stated Marcel Zevenbergen, senior researcher at imec/Holst Centre. “To suppress such leaching, we designed and fabricated an RE with a microfluidic channel as junction and combined it with solid-state iridium oxide (IrOx) and silver chloride (AgCl) electrodes fabricated on a silicon substrate, respectively as indicating electrodes for pH and Cl-. Our tests demonstrated this to be a long-term stable solution with the sensor showing a sensitivity, accuracy and response time that are equal or better than existing solutions, while at the same time being much smaller and potentially less expensive.”
“We are providing groundbreaking sensing and analytics solutions for the IoT,” stated John Baekelmans, Managing Director of imec in The Netherlands. “This new multi-ion sensor is one in a series that Holst Centre is currently developing with its partners to form the senses of the IoT. For each sensor, the aim is to leapfrog the current performance of the state-of-the-art sensors in a mass-producible, wireless, energy optimized and miniaturized package.”
####
About IMEC
Imec is the world-leading research and innovation hub in nano-electronics and digital technologies. The combination of our widely acclaimed leadership in microchip technology and profound software and ICT expertise is what makes us unique. By leveraging our world-class infrastructure and local and global ecosystem of partners across a multitude of industries, we create groundbreaking innovation in application domains such as healthcare, smart cities and mobility, logistics and manufacturing, and energy.
As a trusted partner for companies, start-ups and universities we bring together close to 3,500 brilliant minds from over 70 nationalities. Imec is headquartered in Leuven, Belgium and also has distributed R&D groups at a number of Flemish universities, in the Netherlands, Taiwan, USA, China, and offices in India and Japan. In 2015, imec's revenue (P&L) totaled 415 million euro and of iMinds which is integrated in imec as of September 21, 2016 52 million euro. Further information on imec can be found at www.imec.be
Imec is a registered trademark for the activities of IMEC International (a legal entity set up under Belgian law as a "stichting van openbaar nut”), imec Belgium (IMEC vzw supported by the Flemish Government), imec the Netherlands (Stichting IMEC Nederland, part of Holst Centre which is supported by the Dutch Government), imec Taiwan (IMEC Taiwan Co.) and imec China (IMEC Microelectronics (Shanghai) Co. Ltd.) and imec India (Imec India Private Limited), imec Florida (IMEC USA nanoelectronics design center).
About Holst Centre
Holst Centre is an independent open-innovation R&D centre that develops generic technologies for Wireless Autonomous Transducer Solutions and for Systems-in-Foil. A key feature of Holst Centre is its partnership model with industry and academia around shared roadmaps and programs. It is this kind of cross-fertilization that enables Holst Centre to tune its scientific strategy to industrial needs.
Holst Centre was set up in 2005 by imec (Flanders, Belgium) and TNO (The Netherlands) with support from the Dutch Ministry of Economic Affairs and the Government of Flanders. It is named after Gilles Holst, a Dutch pioneer in Research and Development and first director of Philips Research.
Located on High Tech Campus Eindhoven, Holst Centre benefits from the state-of-the-art on-site facilities. Holst Centre has over 200 employees from around 28 nationalities and a commitment from more than 50 industrial partners. Visit us at www.holstcentre.com.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Paul Wilkie
Business Technology
Havas Formula
t
619 234 0345
m
619 386 4800
w
havasformula.com
a
1215 Cushman Ave, San Diego, CA 92110
Copyright © IMEC
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Internet-of-Things
![]() Nanofibrous metal oxide semiconductor for sensory face November 8th, 2024
Nanofibrous metal oxide semiconductor for sensory face November 8th, 2024
![]() New nanowire sensors are the next step in the Internet of Things January 6th, 2023
New nanowire sensors are the next step in the Internet of Things January 6th, 2023
![]() New chip ramps up AI computing efficiency August 19th, 2022
New chip ramps up AI computing efficiency August 19th, 2022
![]() Lightening up the nanoscale long-wavelength optoelectronics May 13th, 2022
Lightening up the nanoscale long-wavelength optoelectronics May 13th, 2022
Hardware
![]() The present and future of computing get a boost from new research July 21st, 2023
The present and future of computing get a boost from new research July 21st, 2023
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Environment
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Events/Classes
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
![]() A New Blue: Mysterious origin of the ribbontail ray’s electric blue spots revealed July 5th, 2024
A New Blue: Mysterious origin of the ribbontail ray’s electric blue spots revealed July 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers demonstrate co-propagation of quantum and classical signals: Study shows that quantum encryption can be implemented in existing fiber networks January 20th, 2023
Researchers demonstrate co-propagation of quantum and classical signals: Study shows that quantum encryption can be implemented in existing fiber networks January 20th, 2023
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








