Home > Press > Nanosensors on the alert for terrorist threats: Scientists interested in the prospects of gas sensors based on binary metal oxide nanocomposites
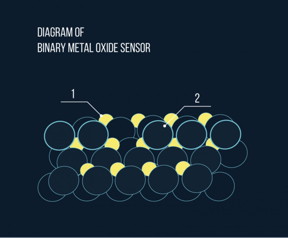 |
| This is a schematic representation of a binary sensor based on two metal oxides, with the nanoparticles of the catalytically active component (1) in yellow and the nanoparticles of the electron donor component (2) represented by the unshaded circles. CREDIT the MIPT press office |
Abstract:
Scientists from the Semenov Institute of Chemical Physics of the Russian Academy of Sciences (ICP RAS) and the Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology (MIPT) have demonstrated that sensors based on binary metal oxide nanocomposites are sensitive enough to identify terrorist threats and detect environmental pollutants. The results of their study have been published in Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical.
Nanosensors on the alert for terrorist threats: Scientists interested in the prospects of gas sensors based on binary metal oxide nanocomposites
Moscow, Russia | Posted on November 5th, 2016Due to rapid industrial growth and the degradation of the environment, there is a growing need for the development of highly effective and selective sensors for pollutant detection. In addition, gas sensors could also be used to monitor potential terrorist threats.
"Choosing the right sensor composition can make a device at least ten times more effective and enable an exceptionally fast response, which is crucial for preventing terrorist attacks," says Prof. Leonid Trakhtenberg of the Department of Molecular and Chemical Physics at MIPT, who is the leader of the research team and the head of the Laboratory of Functional Nanocomposites at ICP RAS.
According to the research findings, the most promising detection systems are binary metal oxide sensors, in which one component provides a high density of conductive electrons and another is a strong catalyst.
A mixed system of that kind has the two necessary components for effective gas detection, viz., an electron donor and a substance "accommodating" the reaction. An additional factor contributing to faster sensor response is the formation of chemisorption centers, i.e., the chemically active spots on the nanocrystals that facilitate gas molecule adsorption.
"We are planning further research into the possibilities for sensor design presented by the multicomponent metal oxide nanocomposites incorporating nanofibers. The development of new effective sensor compositions will be based on a reasonably balanced approach involving both the experimental tests and the advancement of our theoretical understanding of the sensing mechanisms," comments Prof. Trakhtenberg.
A rather promising approach to the development of new gas detection systems is the use of "core-shell type" composite metal oxide nanofibers, where the "core" and the "shell" are composed of two different oxides.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Nicolas
Copyright © Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Law enforcement/Anti-Counterfeiting/Security/Loss prevention
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Homeland Security
![]() The picture of health: Virginia Tech researchers enhance bioimaging and sensing with quantum photonics June 30th, 2023
The picture of health: Virginia Tech researchers enhance bioimaging and sensing with quantum photonics June 30th, 2023
![]() Sensors developed at URI can identify threats at the molecular level: More sensitive than a dog's nose and the sensors don't get tired May 21st, 2021
Sensors developed at URI can identify threats at the molecular level: More sensitive than a dog's nose and the sensors don't get tired May 21st, 2021
![]() Highly sensitive dopamine detector uses 2D materials August 7th, 2020
Highly sensitive dopamine detector uses 2D materials August 7th, 2020
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
Environment
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








