Home > Press > Novel light sources made of 2-D materials
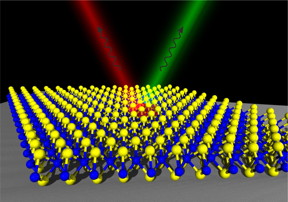 |
| This is an artistic representation of a two-photon source: The monolayer (below) emits exactly two photons of different frequencies under suitable conditions. They are depicted in red and green in the picture. CREDIT (Picture: Karol Winkler) |
Abstract:
So-called monolayers are at the heart of the research activities. These "super materials" (as the prestigious science magazine "Nature" puts it) have been surrounded by a virtual hype in the past ten years. This is because they show great promise to revolutionise many areas of physics.
Novel light sources made of 2-D materials
Wurzburg, Germany | Posted on October 30th, 2016In physics, the term monolayer refers to solid materials of minimum thickness. Occasionally, it is only a single layer of atoms thick; in crystals it can be three or more layers. Experts also speak of two-dimensional materials. In this form, they frequently exhibit unexpected properties that make them interesting for research. The so-called transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDC) are particularly promising. They behave like semiconductors and can be used to manufacture ultra-small and energy-efficient chips, for example.
Moreover, TMDCs are capable of generating light when supplied with energy. Dr. Christian Schneider, Professor Sven Höfling and their research team from the Chair of Technical Physics of the Julius-Maximilians-Universität Würzburg (JMU) in Bavaria, Germany, have harnessed exactly this effect for their experiments.
Experiments started with sticky tape
First, a monolayer was produced using a simple method. This usually involves a piece of sticky tape to peel a multi-layer film from a TMDC crystal in a first step. Using the same procedure, thinner and thinner layers can be stripped from this film. This process is repeated until the material on the tape is only one layer thick.
The researchers then cooled this monolayer down to a temperature of just above absolute zero and excited it with a laser. This causes the monolayer to emit single protons under specific conditions. "We were now able to show that a specific type of excitement produces not one but exactly two photons," Schneider explains. "The light particles are generated in pairs so to speak."
Such two-photon sources are interesting for the following reason: They can be used to transfer information 100% tap-proof. For this purpose, the light particles are entangled with each other - a quantum mechanical process in which their state is interwoven. The state of the first photon then has a direct impact on that of the second photon, regardless of the distance between the two. This fact can be used to encrypt communication channels.
Monolayers enable novel lasers
In a second study, the JMU scientists demonstrated another application option of the exotic monolayers. For this purpose, they mounted a monolayer between two mirrors and again stimulated it with a laser. The radiation excited the TMDC plate to a level that it began to emit photons itself. These were reflected back to the plate by the mirrors where they excited atoms themselves to create new photons.
"We call this process strong coupling," Schneider explains. The light particles are cloned during this process in a manner of speaking. "Light and matter hybridise, forming new quasi particles in the process: the exciton polaritons," the physicist says. For the first time, it has now been possible to detect these polaritons at room temperature in atomic monolayers.
In the medium run, this will open up interesting new applications. The "cloned" photons have similar properties to laser light. But they are manufactured in completely different ways: Ideally, the production of new light particles is self-sustaining after the initial excitation without requiring any additional energy supply. In a laser in contrast, the light-producing material has to be excited energetically from the outside on a permanent basis. This makes the new light source highly energy-efficient. Moreover, it is excellently suited to study certain quantum effects.
Schneider's ERC project bears fruit
In spring 2016, Christian Schneider received one of the coveted ERC Starting Grants of the European Research Council. The European Union thus funds his work on transition metal dichalcogenides with 1.5 million euros in total. The two studies published in the prestigious science journal "Nature Communications" are the first results of the ERC project.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Dr. Christian Schneider
49-931-318-8021
Copyright © University of Wurzburg
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
2 Dimensional Materials
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Optical computing/Photonic computing
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
![]() Nanophotonic platform boosts efficiency of nonlinear-optical quantum teleportation April 25th, 2025
Nanophotonic platform boosts efficiency of nonlinear-optical quantum teleportation April 25th, 2025
![]() Groundbreaking research unveils unified theory for optical singularities in photonic microstructures December 13th, 2024
Groundbreaking research unveils unified theory for optical singularities in photonic microstructures December 13th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








