Home > Press > Mechanism for sodium storage in 2-D material: Tin selenide is an effective host for storing sodium ions, making it a promising material for sodium ion batteries
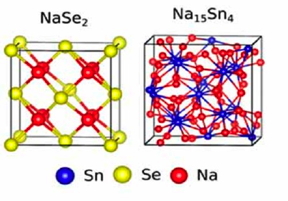 |
| Schematic illustration of the structure at the beginning (left) and the end (right) of the evolution during the sodiation process. Reproduced with permission from ref 1.© 2016 WILEY-VCH Verlag |
Abstract:
The mechanism of sodium ion storage in an important two-dimensional material could be a simpler and less toxic route to cheaper batteries, a team of KAUST researchers discovered.
Mechanism for sodium storage in 2-D material: Tin selenide is an effective host for storing sodium ions, making it a promising material for sodium ion batteries
Thuwal, Saudi Arabia | Posted on October 27th, 2016Lithium ion batteries are the current standard power source for most portable electronic products. When this type of battery is charging, positively-charged lithium ions move from one electrode, the cathode, through an electrolyte to another electrode, which is called the anode. The electrodes are typically porous materials into which the ions become embedded through a process known as intercalation. When the battery is connected to a device, the ions perform the same process in reverse.
However, lithium is neither cheap nor abundant, so scientists are developing sodium ion batteries as a cost-effective alternative for rechargeable sources of power.
In both cases, the choice of electrode material is crucial: it has a significant influence on a battery's energy capacity and its overall lifetime. However, materials that are good electrodes in lithium ion batteries may not be optimal for sodium ion batteries, so there is a need to identify and optimize new materials.
"Two-dimensional materials are potentially attractive anodes for sodium ion batteries due to their large surface area and ability to minimize volume changes during battery operation," said Professor Husam Alshareef from the Material Science and Engineering Program at KAUST. "However, the sodium ion storage mechanism in this emerging class of anodes is not fully understood."
Alshareef and colleagues developed a process for two-dimensional anodes for sodium ion batteries made from tin selenide1. They used a combination of experimental and computational studies to unlock the mechanism by which they store sodium ions.
Tin selenide has been synthesized before, but the production process involves complex chemical reactions performed at high temperatures that can require toxic materials.
Alshareef's team tried a simpler hydrothermal method that uses a solution of sodium hydrogen selenide as a safe and stable source of selenium. They mixed this with tin and selenium and heated it in an oven at 180 degrees Celsius for 24 hours to produce nanosheets.
In-situ spectral studies during battery operation showed that tin selenide stores sodium ions by a two-step process involving both conversion and alloying reactions. This dual mechanism explains the high capacity the team could achieve using SnSe2 anodes.
"The new synthesis process resulted in the highest reported energy density of any transition metal selenide--515 milliampere-hours per gram after 500 charge-discharge cycles," said Fan Zhang, a KAUST Ph.D. student and the lead author of the research paper.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Michelle D'Antoni
Copyright © King Abdullah University of Science and Technology
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
2 Dimensional Materials
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Alliances/Trade associations/Partnerships/Distributorships
![]() Chicago Quantum Exchange welcomes six new partners highlighting quantum technology solutions, from Chicago and beyond September 23rd, 2022
Chicago Quantum Exchange welcomes six new partners highlighting quantum technology solutions, from Chicago and beyond September 23rd, 2022
![]() University of Illinois Chicago joins Brookhaven Lab's Quantum Center June 10th, 2022
University of Illinois Chicago joins Brookhaven Lab's Quantum Center June 10th, 2022
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








