Home > Press > Nanoscale engineering transforms particles into 'LEGO-like' building blocks
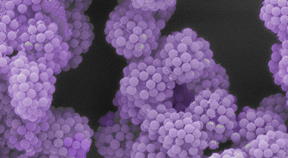 |
| Tiny particles transformed into “LEGO- like” modular building blocks. |
Abstract:
Led by the University of Melbourne and published today in Nature Nanotechnology, the work holds promise for micro and nano scale applications including drug delivery, chemical sensing and energy storage.
Nanoscale engineering transforms particles into 'LEGO-like' building blocks
Melbourne, Australia | Posted on October 12th, 2016Frank Caruso, Professor and ARC Australian Laureate Fellow, Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering said that the team nanoengineered building blocks to tailor the development of advanced materials.
"Nano-objects are difficult to manipulate, as they're too tiny to see directly by eye, far too small to hold, and often have incompatible surfaces for assembling into ordered structures," he said.
"Assembling LEGO bricks into complex shapes is relatively easy, as LEGO studs ensure the blocks stick together wherever you want.
"So we used a similar strategy as a basis for assembling nano-objects into complex architectures by first coating them with a universally adhesive material (a polyphenol) so that they resemble the studs on LEGO bricks.
"This allows for a range of nano-objects to stick together around a template, where the template determines the final shape of the assembled structure," Professor Caruso said.
Different materials can be assembled using this approach. This simple and modular approach has been demonstrated for 15 representative materials to form different sizes, shapes, compositions and functionalities.
Compositions include polymeric particles, metal oxide particles and wires, noble metal nanoparticles, coordination polymer nanowires, nanosheets and nanocubes, and biologicals.
The building blocks can be used to construct complex 3D superstructures, including core-satellite, hollow, hierarchically organised supraparticles, and macroscopic hybrid materials.
"Many previous methods have been limited by particle-specific assembly," Professor Caruso said.
"However, this new polyphenol-based particle approach can be adapted to different functions and allows different building blocks to be assembled into super-structures," he said.
The "studs" in the LEGO brick-like structures, known as C/G studs from the polyphenols, provide a superstructuring process for assembling and inter-locking the building blocks using multiple anchor points.
The "C/G studs" on the building block nanoparticles can further interact with a secondary substrate and/or coordinate with metal ions, interlocking the structures.
This provides a platform for the rapid generation of superstructured assemblies with enhanced chemical diversity and structural flexibility across a wide range of length scales, from nanometres to centimetres.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Anne Rahilly
61-390-355-380
Copyright © University of Melbourne
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
Chemistry
![]() Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








