Home > Press > More stable qubits in perfectly normal silicon
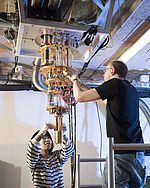 |
Abstract:
The power of future quantum computers stems from the use of qubits, or quantum bits, which do not have to be either 0 or 1, but can also be 0 and 1 at the same time. It is not yet clear on which technology these qubits in quantum computers will be based, but qubits based on electron spins are looking more and more promising. It was thought that these could only be produced in the expensive semiconductor material gallium arsenide, but researchers have now discovered that the more common material silicon, the basic material of modern computer chips, is even better. Researchers from Delft, the University of Wisconsin and Ames Laboratory, led by Prof. Lieven Vandersypen of TU Delft's QuTech discovered that the stability of qubits could be maintained 100 times more effectively in silicon than in gallium arsenide. They publishing their research in PNAS this week.
More stable qubits in perfectly normal silicon
Delft, The Netherlands | Posted on October 11th, 2016Fragile
Because qubits can be both 1 and 0 simultaneously, a quantum computer will be able to tackle computing problems that are out of reach of the current supercomputers. The main issue for researchers is that this superposition is very fragile. 'Two numbers are very important for qubits,' explains research leader Lieven Vandersypen. 'The length of time the superposition can be maintained before it spontaneously reverts to 1 or 0 is critical for an effectively functioning quantum computer. In gallium arsenide, this is about 10 nanoseconds, but in silicon we have achieved a factor of 100 longer. Using smart technologies we were able to stretch this to 0.4 milliseconds. Although a coherence time of 0.4 milliseconds may not sound very long, for a computer it is nearly an eternity. Moreover, the gate fidelity in silicon is 10-100 times better. The gate fidelity is the measure of whether an operation you perform on a qubit will actually work.'
Silicon
The researchers used 'standard' silicon, an extremely cheap material of which there is an almost infinite supply: it is the main ingredient of sand. Earlier research by the University of New South Wales in Australia demonstrated that isotopically purified silicon-28 can produce even better results. "Silicon naturally contains three isotopes, including the common form Si-28, and the less common form with atomic number 29. The latter form has been proven to degrade the coherence and gate fidelity considerably. Researchers believe that replacing gallium arsenide with silicon will be extremely important for the design of the quantum computer. The required technology for fabricating nanostructures in silicon has already reached an advanced stage in chip technology, and now, as the researchers hoped, silicon also proves to be a better qubit material.
Scaling up
Researchers of TU Delft are collaborating intensively with other researchers, among others from Intel Corporation, who joined a partnership with QuTech last year. The greatest challenge for quantum technologists now is to scale up the various qubits for use in circuits of multiple interplaying qubits. 'At least hundreds of qubits - and preferably many more - will need to work together to make a working quantum computer,' says Vandersypen.
###
The research published in PNAS was supported by the Dutch Organization for Fundamental Research on Matter (FOM)
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Lieven Vandersypen
31-152-782-469
Copyright © TU Delft
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Quantum Computing
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








