Home > Press > Metamaterial uses light to control its motion
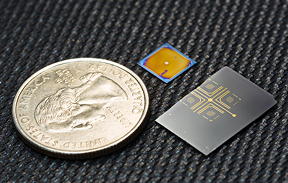 |
| Optically-driven mechanical oscillator fabricated using a plasmomechanical metamaterial. |
Abstract:
Researchers have designed a device that uses light to manipulate its mechanical properties. The device, which was fabricated using a plasmomechanical metamaterial, operates through a unique mechanism that couples its optical and mechanical resonances, enabling it to oscillate indefinitely using energy absorbed from light.
Metamaterial uses light to control its motion
San Diego, CA | Posted on October 10th, 2016This work demonstrates a metamaterial-based approach to develop an optically-driven mechanical oscillator. The device can potentially be used as a new frequency reference to accurately keep time in GPS, computers, wristwatches and other devices, researchers said. Other potential applications that could be derived from this metamaterial-based platform include high precision sensors and quantum transducers. The research was published Oct. 10 in the journal Nature Photonics.
Researchers engineered the metamaterial-based device by integrating tiny light absorbing nanoantennas onto nanomechanical oscillators. The study was led by Ertugrul Cubukcu, a professor of nanoengineering and electrical engineering at the University of California San Diego. The work, which Cubukcu started as a faculty member at the University of Pennsylvania and is continuing at the Jacobs School of Engineering at UC San Diego, demonstrates how efficient light-matter interactions can be utilized for applications in novel nanoscale devices.
Metamaterials are artificial materials that are engineered to exhibit exotic properties not found in nature. For example, metamaterials can be designed to manipulate light, sound and heat waves in ways that can’t typically be done with conventional materials.
Metamaterials are generally considered “lossy” because their metal components absorb light very efficiently. “The lossy trait of metamaterials is considered a nuisance in photonics applications and telecommunications systems, where you have to transmit a lot of power. We’re presenting a unique metamaterials approach by taking advantage of this lossy feature,” Cubukcu said.
Click Here for a HighResolution Version
Cross-section of the metamaterial-based device. The top is a bilayer gold/silicon nitride membrane containing an array of cross-shaped nanoantennas etched into the gold layer. The bottom is a metal reflector that is separated from the gold/silicon nitride bilayer by a three-micron-wide air gap. Image courtesy of UC San Diego Nanoengineered Photonics Group.
The device in this study resembles a tiny capacitor—roughly the size of a quarter—consisting of two square plates measuring 500 microns by 500 microns. The top plate is a bilayer gold/silicon nitride membrane containing an array of cross-shaped slits—the nanoantennas—etched into the gold layer. The bottom plate is a metal reflector that is separated from the gold/silicon nitride bilayer by a three-micron-wide air gap.
When light is shined upon the device, the nanoantennas absorb all of the incoming radiation from light and convert that optical energy into heat. In response, the gold/silicon nitride bilayer bends because gold expands more than silicon nitride when heated. The bending of the bilayer alters the width of the air gap separating it from the metal reflector. This change in spacing causes the bilayer to absorb less light and as a result, the bilayer bends back to its original position. The bilayer can once again absorb all of the incoming light and the cycle repeats over and over again.
The device relies on a unique hybrid optical resonance known as the Fano resonance, which emerges as a result of the coupling between two distinct optical resonances of the metamaterial. The optical resonance can be tuned “at will” by applying a voltage.
The researchers also point out that because the plasmomechanical metamaterial can efficiently absorb light, it can function under a broad optical resonance. That means this metamaterial can potentially respond to a light source like an LED and won’t need a strong laser to provide the energy.
“Using plasmonic metamaterials, we were able to design and fabricate a device that can utilize light to amplify or dampen microscopic mechanical motion more powerfully than other devices that demonstrate these effects. Even a non-laser light source could still work on this device,” said Hai Zhu, a former graduate student in Cubukcu’s lab and first author of the study.
“Optical metamaterials enable the chip-level integration of functionalities such as light-focusing, spectral selectivity and polarization control that are usually performed by conventional optical components such as lenses, optical filters and polarizers. Our particular metamaterial-based approach can extend these effects across the electromagnetic spectrum,” said Fei Yi, a postdoctoral researcher who worked in Cubukcu's lab.
###
Full paper: “Plasmonic metamaterial absorber for broadband manipulation of mechanical resonances.” Authors of the study are: Hai Zhu and Fei Yi, University of Pennsylvania; and Ertugrul Cubukcu, UC San Diego.
This work was supported by the National Science Foundation Electrical, Communications and Cyber Systems division (grant ECCS-1632797).
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Liezel Labios
Jacobs School of Engineering
Phone: 858-246-1124
Copyright © University of California, San Diego
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Hardware
![]() The present and future of computing get a boost from new research July 21st, 2023
The present and future of computing get a boost from new research July 21st, 2023
![]() A Carbon Nanotube Microprocessor Mature Enough to Say Hello: Three new breakthroughs make commercial nanotube processors possible March 2nd, 2020
A Carbon Nanotube Microprocessor Mature Enough to Say Hello: Three new breakthroughs make commercial nanotube processors possible March 2nd, 2020
![]() Powering the future: Smallest all-digital circuit opens doors to 5 nm next-gen semiconductor February 11th, 2020
Powering the future: Smallest all-digital circuit opens doors to 5 nm next-gen semiconductor February 11th, 2020
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Nanoelectronics
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
![]() Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
![]() Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
Quantum nanoscience
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








