Home > Press > Neutron crystallography aids in drug design
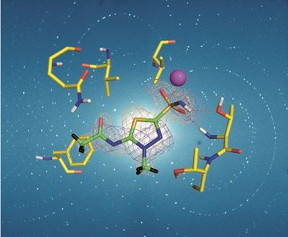 |
| Neutron crystallography aids in drug design. CREDIT: M. P. Blakeley |
Abstract:
Neutron crystallography is an important complementary technique to X-ray crystallography since it provides details of the hydrogen atom and proton positions in biological molecules. Furthermore, as neutrons are a non-destructive probe, the resulting structures are free from radiation damage even at room temperature. Knowledge of H-bonding networks, water molecule orientations and protonation states, along with details of hydrophobic and electrostatic interactions, can prove vital towards a better understanding of many biological processes, such as enzyme mechanisms and can help guide structure-based drug design.
Neutron crystallography aids in drug design
Chester, UK | Posted on September 9th, 2016The first neutron crystallography study of a clinically used drug bound to its target was that of acetazolamide (AZM), a sulphonamide, which binds with high affinity to human carbonic anhydrase isoform II. Human carbonic anhydrases (hCA) are zinc metalloenzymes that catalyse the interconversion of CO2 and H2O to HCO3- and H+, an important reaction for many physiological processes including respiration, fluid secretion and pH regulation. As such hCA isoforms are prominent clinical targets for treating various diseases, such as glaucoma and epilepsy. hCA II is one of 12 catalytically active isoforms and, due to sequence conservation between them, substantial off-target binding to other isoforms occurs, reducing drug efficiency and causing side effects. Hence, there is a need to design effective hCA isoform-specific drugs. Over 400 X-ray crystal structures have been determined for hCA II, with around half of these in complex with inhibitors, yet despite the large amount of X-ray structural data available, key details regarding the H-atom positions of the protein and solvent and the charged state of the bound inhibitor were, until recently, missing for all but the hCA II/acetazolamide complex.
In the September issue of IUCrJ [Aggarwal et al. (2016), IUCrJ. 3, 319-325; doi:10.1107/S2052252516010514] McKenna and co-workers describe X-ray and neutron crystallographic studies of hCA II in complex with the inhibitor methoazolamide (MZM) providing missing details of the H-bonding and hydrophobic interactions in the complex, and identifying the charged state of MZM. They then compare the binding of AZM and MZM in the room-temperature neutron structures and discuss the observed differences in binding in terms of the enthalpic and entropic contributions to drug binding, suggesting that in the case of MZM, hydrophobic forces perhaps compensate for the loss of an extensive H-bonding network.
Over the past few years, a growing number of neutron structures have been deposited in the Protein Data Bank, including a number of other examples of enzyme-drug complexes. Although the overall number of neutron structures is still relatively small, there are growing numbers of examples for which neutron crystallography has provided the answers to questions that have remained elusive using other techniques.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Dr. Jonathan Agbenyega
44-124-434-2878
Copyright © International Union of Crystallography
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Crystallography
![]() First measurement of electron energy distributions, could enable sustainable energy technologies June 5th, 2020
First measurement of electron energy distributions, could enable sustainable energy technologies June 5th, 2020
![]() How to trick electrons to see the hidden face of crystals: Researchers try a trick for complete 3D analysis of submicron crystals August 3rd, 2019
How to trick electrons to see the hidden face of crystals: Researchers try a trick for complete 3D analysis of submicron crystals August 3rd, 2019
![]() 3-D-printed jars in ball-milling experiments June 29th, 2017
3-D-printed jars in ball-milling experiments June 29th, 2017
![]() Novel nozzle saves crystals: Double flow concept widens spectrum for protein crystallography March 17th, 2017
Novel nozzle saves crystals: Double flow concept widens spectrum for protein crystallography March 17th, 2017
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








