Home > Press > New electrical energy storage material shows its power: Nanomaterial combines attributes of both batteries and supercapacitors
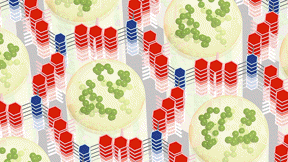 |
| he best of both worlds. A new nanomaterial acts as both battery and supercapacitor: A conductive polymer (green) formed inside the small holes of a hexagonal framework (red and blue) works with the framework to store electrical energy rapidly and efficiently. Credit: William Dichtel, Northwestern University |
Abstract:
A powerful new material developed by Northwestern University chemist William Dichtel and his research team could one day speed up the charging process of electric cars and help increase their driving range.
A Northwestern University chemist and his research team have developed a modified covalent organic framework (COF) material that can power a light-emitting diode.
CREDIT: American Chemical Society
New electrical energy storage material shows its power: Nanomaterial combines attributes of both batteries and supercapacitors
Evanston, IL | Posted on August 25th, 2016An electric car currently relies on a complex interplay of both batteries and supercapacitors to provide the energy it needs to go places, but that could change.
"Our material combines the best of both worlds -- the ability to store large amounts of electrical energy or charge, like a battery, and the ability to charge and discharge rapidly, like a supercapacitor," said Dichtel, a pioneer in the young research field of covalent organic frameworks (COFs).
Dichtel and his research team have combined a COF -- a strong, stiff polymer with an abundance of tiny pores suitable for storing energy -- with a very conductive material to create the first modified redox-active COF that closes the gap with other older porous carbon-based electrodes.
"COFs are beautiful structures with a lot of promise, but their conductivity is limited," Dichtel said. "That's the problem we are addressing here. By modifying them -- by adding the attribute they lack -- we can start to use COFs in a practical way."
And modified COFs are commercially attractive: COFs are made of inexpensive, readily available materials, while carbon-based materials are expensive to process and mass-produce.
Dichtel, the Robert L. Letsinger Professor of Chemistry at the Weinberg College of Arts and Sciences, is presenting his team's findings today (Aug. 24) at the American Chemical Society (ACS) National Meeting in Philadelphia. Also today, a paper by Dichtel and co-authors from Northwestern and Cornell University was published by the journal ACS Central Science.
To demonstrate the new material's capabilities, the researchers built a coin-cell battery prototype device capable of powering a light-emitting diode for 30 seconds.
The material has outstanding stability, capable of 10,000 charge/discharge cycles, the researchers report. They also performed extensive additional experiments to understand how the COF and the conducting polymer, called poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) or PEDOT, work together to store electrical energy.
Dichtel and his team made the material on an electrode surface. Two organic molecules self-assembled and condensed into a honeycomb-like grid, one 2-D layer stacked on top of the other. Into the grid's holes, or pores, the researchers deposited the conducting polymer.
Each pore is only 2.3 nanometers wide, but the COF is full of these useful pores, creating a lot of surface area in a very small space. A small amount of the fluffy COF powder, just enough to fill a shot glass and weighing the same as a dollar bill, has the surface area of an Olympic swimming pool.
The modified COF showed a dramatic improvement in its ability to both store energy and to rapidly charge and discharge the device. The material can store roughly 10 times more electrical energy than the unmodified COF, and it can get the electrical charge in and out of the device 10 to 15 times faster.
"It was pretty amazing to see this performance gain," Dichtel said. "This research will guide us as we investigate other modified COFs and work to find the best materials for creating new electrical energy storage devices."
###
The research was conducted at Cornell University, where Dichtel was a faculty member until this summer, when he moved to Northwestern.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Megan Fellman
847-491-3115
Copyright © Northwestern University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








