Home > Press > Enhanced electron doping on iron superconductors discovered: IBS Centre for Correlated Electron Systems revises existing theories by raising the temperature for superconductivity
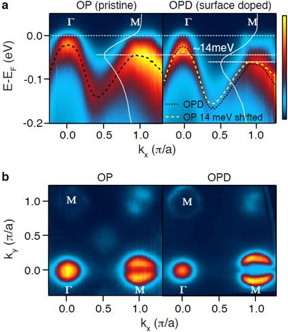 |
| Before and after the attachment of alkaline metals to the surface of iron-based, pniktogen superconductors.
(a) Quantity of momentum of electrons (X) and kinetic energy of electrons (Y) before and after the electron doping : electron doping has changed the distribution of electron kinetic energy. (b) Fermi surface data before and after the electron doping: nesting condition has been weakened. CREDIT: IBS |
Abstract:
The IBS research team headed by the associate director of CCES, KIM Chang Young, presented the possibility of unifying theories to explain the working mechanism of iron- based superconductors. Their research was published in Nature Materials on August 16th. Superconductors are a relatively new concept; they were brought to prominence in the late 80's when two Nobel Prize winners discovered a new superconducting material. The basic principle of superconductivity arises when a superconducting material is cooled to a fairly low critical temperature allowing an electric current to flow without resistance.
Enhanced electron doping on iron superconductors discovered: IBS Centre for Correlated Electron Systems revises existing theories by raising the temperature for superconductivity
Daejeon, Korea | Posted on August 17th, 2016Building on a Nobel Prize
The Nobel Prize winners reported their superconducting material - oxides which contain copper and rare earth metals - becomes a superconducting material below -250° Celsius, higher than the previous temperature of -269° Celsius. This led to a boom in developing similar materials for commercial use. Today's research has moved on greatly; oxides are replaced with iron-based superconductors which are cheaper to mass produce and also permit a current to flow unabated. To understand the working mechanism of iron-based superconductors scientists have to significantly raise the transition temperatures to source the reason for the increase. Many researchers initially work on the assumption that the nesting effect is a dominant factor, especially in the case of pnictide superconductors {PSD}. Later, scientists discovered another type of superconductor, chalogenide superconductors {CSD}. Since it turned out that CSD is not subject to the nesting effect, the discovery of CSD generated controversy on the mechanism of their superconductivity. The nesting effect states when the surface temperature is increased, electrons become unstable thereby altering their properties both electrically and magnetically, allowing conductors to turn into superconductors.
Rewriting theories with peripheral electrons
Working under the assumption that a strong nesting effect in PSD corresponds to high temperature, the CCES team used potassium (K) and sodium (Na), two alkaline metals with peripheral electrons, thereby facilitating an easy transfer of electrons to other metals. They heated K and Na in a vacuumed environment to excite their atoms whereby the atoms attached to the surface of PSD, which have a lower temperature than the K and Na. As a result electron doping took place on the surface of PSD. The IBS team measured the momentum and kinetic energy of electrons and revealed, for the first time, that there is, in fact, no correlation between superconducting transition temperature and the nesting effect in PSD as is the case in CSD.
Associate director Kim Chang Young said, "Up to now the prevailing theory of PSD and CSD have been thought of as two different systems. Our research is a starting point to confirm that those two superconductors have the same working mechanism, we have laid a cornerstone for the discovery of iron-based superconductors, whose production cost is low and has no restraints in its current."
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Carol Kim
82-428-788-133
Copyright © Institute for Basic Science
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Superconductivity
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








