Home > Press > Tiny works of art with great potential: New materials for the construction of metal-organic 2-dimensional quasicrystals
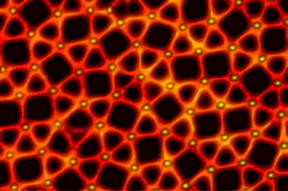 |
| This is a scanning tunneling microscopic image of the quasicrystalline network built up with europium atoms linked with para-quaterphenyl-dicarbonitrile. CREDIT: J. I. Urgel / TUM |
Abstract:
Unlike classical crystals, quasicrystals do not comprise periodic units, even though they do have a superordinate structure. The formation of the fascinating mosaics that they produce is barely understood. In the context of an international collaborative effort, researchers at the Technical University of Munich (TUM) have now presented a methodology that allows the production of two-dimensional quasicrystals from metal-organic networks, opening the door to the development of promising new materials.
Tiny works of art with great potential: New materials for the construction of metal-organic 2-dimensional quasicrystals
Munich, Germany | Posted on July 15th, 2016Physicist Daniel Shechtman merely put down three question marks in his laboratory journal, when he saw the results of his latest experiment one day in 1982. He was looking at a crystalline pattern that was considered impossible at the time. According to the canonical tenet of the day, crystals always had so-called translational symmetry. They comprise a single basic unit, the so-called elemental cell, that is repeated in the exact same form in all spatial directions.
Although Shechtman's pattern did contain global symmetry, the individual building blocks could not be mapped onto each other merely by translation. The first quasicrystal had been discovered. In spite of partially stark criticism by reputable colleagues, Shechtman stood fast by his new concept and thus revolutionized the scientific understanding of crystals and solid bodies. In 2011 he ultimately received the Nobel Prize in Chemistry. To this day, both the basic conditions and mechanisms by which these fascinating structures are formed remain largely shrouded in mystery.
A toolbox for quasicrystals
Now a group of scientists led by Wilhelm Auwärter and Johannes Barth, both professors in the Department of Surface Physics at TU Munich, in collaboration with Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST, Prof. Nian Lin, et al) and the Spanish research institute IMDEA Nanoscience (Dr. David Écija), have developed a new basis for producing two-dimensional quasicrystals, which might bring them a good deal closer to understanding these peculiar patterns.
The TUM doctoral candidate José Ignacio Urgel made the pioneering measurements in the course of a research fellowship at HKUST. "We now have a new set of building blocks that we can use to assemble many different new quasicrystalline structures. This diversity allows us to investigate on how quasicrystals are formed," explain the TUM physicists.
The researchers were successful in linking europium - a metal atom in the lanthanide series - with organic compounds, thereby constructing a two-dimensional quasicrystal that even has the potential to be extended into a three-dimensional quasicrystal. To date, scientists have managed to produce many periodic and in part highly complex structures from metal-organic networks, but never a quasicrystal.
The researchers were also able to thoroughly elucidate the new network geometry in unparalleled resolution using a scanning tunnelling microscope. They found a mosaic of four different basic elements comprising triangles and rectangles distributed irregularly on a substrate. Some of these basic elements assembled themselves to regular dodecagons that, however, cannot be mapped onto each other through parallel translation. The result is a complex pattern, a small work of art at the atomic level with dodecagonal symmetry.
Interesting optical and magnetic properties
In their future work, the researchers are planning to vary the interactions between the metal centers and the attached compounds using computer simulation and experiments in order to understand the conditions under which two-dimensional quasicrystals form. This insight could facilitate the future development of new tailored quasicrystalline layers.
These kinds of materials hold great promise. After all, the new metal-organic quasicrystalline networks may have properties that make them interesting in a wide variety of application. "We have discovered a new playing field on which we can not only investigate quasicrystallinity, but also create new functionalities, especially in the fields of optics and magnetism," says Dr. David Écija of IMDEA Nanoscience.
For one, scientists could one day use the new methodology to create quasicrystalline coatings that influence photons in such a manner that they are transmitted better or that only certain wavelengths can pass through the material.
In addition, the interactions of the lanthanide building blocks in the new quasicrystals could facilitate the development of magnetic systems with very special properties, so-called "frustrated systems". Here, the individual atoms in a crystalline grid interfere with each other in a manner that prevents grid points from achieving a minimal energy state. The result: exotic magnetic ground states that can be investigated as information stores for future quantum computers.
###
The research was funded by the European Research Council (Advanced Grant MolArt), the Spanish Ramón and Cajal Program, the Comunidad de Madrid, the Hong Kong Research Grants Council, and the TUM-HKUST Sponsorship Scheme for Targeted Strategic Partnerships.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Dr. Andreas Battenberg
49-892-891-0510
Copyright © Technical University of Munich (TUM)
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
2 Dimensional Materials
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Quantum Computing
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Nanoelectronics
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
![]() Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
![]() Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








