Home > Press > University of Illinois researchers demonstrate tunable wetting and adhesion of graphene
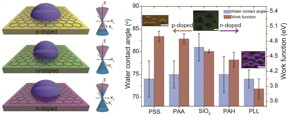 |
| Doping-induced tunable wetting of graphene. CREDIT: University of Illinois |
Abstract:
Researchers from the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign have demonstrated doping-induced tunable wetting and adhesion of graphene, revealing new and unique opportunities for advanced coating materials and transducers.
University of Illinois researchers demonstrate tunable wetting and adhesion of graphene
Urbana, IL | Posted on July 9th, 2016"Our study suggests that the doping-induced modulation of the charge carrier density in graphene influences its wettability and adhesion," explained SungWoo Nam, an assistant professor in the Department of Mechanical Science and Engineering at Illinois. "This work investigates this new doping-induced tunable wetting phenomena which is unique to graphene and potentially other 2D materials in complementary theoretical and experimental investigations."
Graphene, being optically transparent and possessing superior electrical and mechanical properties, can revolutionize the fields of surface coatings and electrowetting displays, according to the researchers. A material's wettability (i.e. interaction with water) is typically constant in the absence of external influence and are classified as either water-loving (hydrophilic) or water-repelling (hydrophobic; water beads up on the surface). Depending on the specific application, a choice between either hydrophobic or hydrophilic material is required. For electrowetting displays, for example, the hydrophilic characteristics of display material is enhanced with the help of a constant externally impressed electric current.
"What makes graphene special is that, unlike conventional bulk materials, it displays tunable surface wetting characteristics due to a change in its electron density, or by doping," said Ali Ashraf, a graduate student researcher and first author of the paper, "Doping-Induced Tunable Wettability and Adhesion of Graphene," appearing in Nano Letters. "Our collaborative research teams have discovered that while graphene behaves typically as a hydrophobic material (due to presence of strongly held air-borne contamination on its surface), its hydrophobicity can be readily changed by changing electron density.
"Our study shows that graphene demonstrates tunable wettability -- switchable hydrophobic and hydrophilic behavior -- when its electron density is changed by subsurface charged polymers and metals (a.k.a. doping)," Ashraf added. "This finding sheds lights on previous unclear links between quantum-level charge transfer and macroscopic surface wettability for graphene. This exciting finding opens new doors of possibility for tunable surface coating and electrowetting displays without continuous external electric current supply, which will translate into significant energy savings."
"In addition, we investigated another closely related property -- surface adhesion," Nam said. "We observed changes in electron density of graphene leads to a change in adhesion, which determines how graphene interacts with other hydrophobic and hydrophilic molecules, which is important for graphene-based chemical and biosensors. Our finding suggests that it is possible to make reusable, self-cleaning graphene sensors that can first interact with hydrophobic molecules for detection, and then separates from them (i.e. cleans itself) by enhanced hydrophilicity via electron density modulation."
###
In addition to Nam and Ashraf, co-authors include Yanbin Wu, Michael Cai Wang, Keong Yong, Tao Sun, Yuhang Jing, Richard T. Haasch, and Narayana Aluru, a professor of mechanical science and engineering, whose research group carried out theoretical modeling of this new experimental observation in this study.
The authors note that our work independently demonstrates and further supports similar findings reported in Hong et al. (DOI: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.6b01594), showing doping-induced wettability modulation of graphene.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
SungWoo Nam
217-300-0267
Copyright © University of Illinois College of Engineering
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
2 Dimensional Materials
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() Closing the gaps — MXene-coating filters can enhance performance and reusability February 28th, 2025
Closing the gaps — MXene-coating filters can enhance performance and reusability February 28th, 2025
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Hardware
![]() The present and future of computing get a boost from new research July 21st, 2023
The present and future of computing get a boost from new research July 21st, 2023
![]() A Carbon Nanotube Microprocessor Mature Enough to Say Hello: Three new breakthroughs make commercial nanotube processors possible March 2nd, 2020
A Carbon Nanotube Microprocessor Mature Enough to Say Hello: Three new breakthroughs make commercial nanotube processors possible March 2nd, 2020
![]() Powering the future: Smallest all-digital circuit opens doors to 5 nm next-gen semiconductor February 11th, 2020
Powering the future: Smallest all-digital circuit opens doors to 5 nm next-gen semiconductor February 11th, 2020
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Nanoelectronics
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
![]() Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
![]() Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








