Home > Press > Tailored DNA shifts electrons into the 'fast lane': DNA nanowire improved by altering sequences
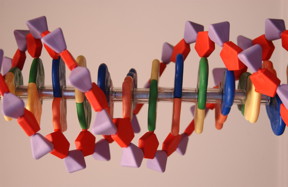 |
| Each ribboning strand of DNA in our bodies is built from stacks of four molecular bases, shown here as blocks of yellow, green, blue and orange, whose sequence encodes detailed operating instructions for the cell. New research shows that tinkering with the order of these bases can also be used to tune the electrical conductivity of nanowires made from DNA. CREDIT: Maggie Bartlett, NHGRI |
Abstract:
DNA molecules don't just code our genetic instructions. They can also conduct electricity and self-assemble into well-defined shapes, making them potential candidates for building low-cost nanoelectronic devices.
Tailored DNA shifts electrons into the 'fast lane': DNA nanowire improved by altering sequences
Durham, NC | Posted on June 22nd, 2016A team of researchers from Duke University and Arizona State University has shown how specific DNA sequences can turn these spiral-shaped molecules into electron "highways," allowing electricity to more easily flow through the strand.
The results may provide a framework for engineering more stable, efficient and tunable DNA nanoscale devices, and for understanding how DNA conductivity might be used to identify gene damage. The study appears online June 20 in Nature Chemistry.
Scientists have long disagreed over exactly how electrons travel along strands of DNA, says David N. Beratan, professor of chemistry at Duke University and leader of the Duke team. Over longer distances, they believe electrons travel along DNA strands like particles, "hopping" from one molecular base or "unit" to the next. Over shorter distances, the electrons use their wave character, being shared or "smeared out" over multiple bases at once.
But recent experiments lead by Nongjian Tao, professor of electrical engineering at Arizona State University and co-author on the study, provided hints that this wave-like behavior could be extended to longer distances.
This result was intriguing, says Duke graduate student and study lead author Chaoren Liu, because electrons that travel in waves are essentially entering the "fast lane," moving with more efficiency than those that hop.
"In our studies, we first wanted to confirm that this wave-like behavior actually existed over these lengths," Liu said. "And second, we wanted to understand the mechanism so that we could make this wave-like behavior stronger or extend it to even longer distances."
DNA strands are built like chains, with each link comprising one of four molecular bases whose sequence codes the genetic instructions for our cells. Using computer simulations, Beratan's team found that manipulating these same sequences could tune the degree of electron sharing between bases, leading to wave-like behavior over longer or shorter distances. In particular, they found that alternating blocks of five guanine (G) bases on opposite DNA strands created the best construct for long-range wave-like electronic motions.
The team theorizes that creating these blocks of G bases causes them to all "lock" together so the wave-like behavior of the electrons is less likely to be disrupted by random wiggling in the DNA strand.
"We can think of the bases being effectively linked together so they all move as one," Liu said. "This helps the electron be shared within the blocks."
The Tao group confirmed these theoretical predictions using break junction experiments, tethering short DNA strands built from alternating blocks of three to eight guanine bases between two gold electrodes and measuring the amount of electrical charge flowing through the molecules.
The results shed light on a long-standing controversy over the exact nature of the electron transport in DNA, Beratan says. They might also provide insight into the design of tunable DNA nanoelectronics, and into the role of DNA electron transport in biological systems.
"This theoretical framework shows us that the exact sequence of the DNA helps dictate whether electrons might travel like particles, and when they might travel like waves," Beratan said. "You could say we are engineering the wave-like personality of the electron."
###
Other authors include Yuqi Zhang and Peng Zhang of Duke University and Limin Xiang and Yueqi Li of Arizona State University.
This research was supported by grants from the Office of Naval Research (N00014-11-1-0729) and the National Science Foundation (DMR-1413257).
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Kara J. Manke
919-681-8064
Copyright © Duke University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Nanoelectronics
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
![]() Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
![]() Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








