Home > Press > Spintronics for future information technologies: Spin currents in topological insulators controlled
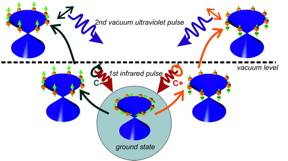 |
| The illustration depicts the characteristic spin orientation (arrows) of electrons in a topological insulator (below). Using an initial circular polarised laser pulse, the spins are excited and point up or down. This can be proven by a second linearly polarised laser pulse (above). CREDIT: HZB |
Abstract:
They thereby demonstrated that this class of materials is suitable for data processing based on spin. The work has been published in the renowned periodical Physical Review B and was selected as "Editor's Suggestion" article.
Spintronics for future information technologies: Spin currents in topological insulators controlled
Berlin, Germany | Posted on May 2nd, 2016Future information technologies should employ considerably less energy for processing data. One exciting class of materials for this comprises topological insulators. Topological insulators are distinguished by their electrons at the surface being extremely mobile, while the bulk material within is an insulator and does not conduct. Since electrons also simultaneously carry a magnetic moment (spin), topological insulators might also make "spintronic" components feasible. Spintronic components would not be based on the movement of charge carriers like electrons (as in semiconductor components), but instead on the transport or manipulation of their spins. This would require considerably less energy.
An international team headed by HZB physicist Jaime Sánchez-Barriga has now shown how the spins of the electrons in topological insulators can be controlled. The team investigated samples of antimony-telluride, a topological insulator, using circularly polarised laser light. They were able to initiate and direct currents of electrons whose spins were oriented in parallel (i. e., spin-polarised currents) using the "rotational direction" of the laser light. In addition, they were successful in changing the orientation of the spins as well. The team was made up of experimentalists from the Max Born Institute in Berlin and Lomonossow University Moscow, together with theoreticians from Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München (LMU). The work has been published in the renowned journal Physical Review B and was selected as "Editor's Suggestion" article.
"If you were to utilise magnetically doped topological insulators, you could also probably store this spin information", explains Oliver Rader, who heads the research group for green spintronics at HZB. "To investigate this however, and also be able to explore the dynamic behaviour of the magnetic moments in particular, ultra-short light pulses in the soft X-ray region are needed. These kinds of experiments can become standard with the planned upgrade of the BESSY II synchrotron source to BESSY-VSR", he hopes.
###
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Dr. Jaime Sánchez-Barriga
49-308-062-15695
Copyright © Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin für Materialien und Energie
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
Quantum Physics
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Spintronics
![]() Quantum materials: Electron spin measured for the first time June 9th, 2023
Quantum materials: Electron spin measured for the first time June 9th, 2023
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Quantum Computing
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








