Home > Press > Nanomaterial to drive new generation of solar cells: ANU media release
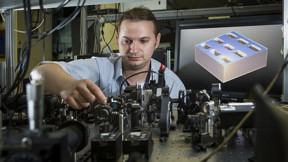 |
| Dr. Kruk is next to a diagram of the metamaterial structure.
Image Stuart Hay, ANU |
Abstract:
Physicists have discovered radical new properties in a nanomaterial which opens new possibilities for highly efficient thermophotovoltaic cells, which could one day harvest heat in the dark and turn it into electricity.
Nanomaterial to drive new generation of solar cells: ANU media release
Canberra, Australia | Posted on April 19th, 2016Physicists have discovered radical new properties in a nanomaterial which opens new possibilities for highly efficient thermophotovoltaic cells, which could one day harvest heat in the dark and turn it into electricity.
The research team from the Australian National University (ARC Centre of Excellence CUDOS) and the University of California Berkeley demonstrated a new artificial material, or metamaterial, that glows in an unusual way when heated.
The findings could drive a revolution in the development of cells which convert radiated heat into electricity, known as thermophotovoltaic cells.
"Thermophotovoltaic cells have the potential to be much more efficient than solar cells," said Dr Sergey Kruk from the ANU Research School of Physics and Engineering.
"Our metamaterial overcomes several obstacles and could help to unlock the potential of thermophotovoltaic cells."
Thermophotovoltaic cells have been predicted to be more than two times more efficient than conventional solar cells. They do not need direct sunlight to generate electricity, and instead can harvest heat from their surroundings in the form of infrared radiation.
They can also be combined with a burner to produce on-demand power or can recycle heat radiated by hot engines.
The research is published in Nature Communications.
The team's metamaterial, made of tiny nanoscopic structures of gold and magnesium fluoride, radiates heat in specific directions. The geometry of the metamaterial can also be tweaked to give off radiation in specific spectral range, in contrast to standard materials that emit their heat in all directions as a broad range of infrared wavelengths. This makes it ideal for use as an emitter paired with a thermophotovoltaic cell.
The project started when Dr Kruk predicted the new metamaterial would have these surprising properties. The ANU team then worked with scientists at the University of California Berkeley, who have unique expertise in manufacturing such materials.
"To fabricate this material the Berkeley team were operating at the cutting edge of technological possibilities," Dr Kruk said.
"The size of individual building block of the metamaterial is so small that we could fit more than twelve thousand of them on the cross-section of a human hair."
The key to the metamaterial's remarkable behaviour is its novel physical property, magnetic hyperbolic dispersion. Dispersion describes the interactions of light with materials and can be visualized as a three-dimensional surface representing how electromagnetic radiation propagates in different directions. For natural materials, such as glass or crystals the dispersion surfaces have simple forms, spherical or ellipsoidal.
The dispersion of the new metamaterial is drastically different and takes hyperbolic form. This arises from the material's remarkably strong interactions with the magnetic component of light.
The efficiency of thermovoltaic cells based on the metamaterial can be further improved if the emitter and the receiver have just a nanoscopic gap between them. In this configuration, radiative heat transfer between them can be more than ten times more efficient than between conventional materials.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Dr. Sergey Kruk
61-261-259-074
Copyright © Australian National University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
Solar/Photovoltaic
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
![]() Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








